* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Myers` Psychology for AP*
Forensic psychology wikipedia , lookup
Personality psychology wikipedia , lookup
Health psychology wikipedia , lookup
Dialogical self wikipedia , lookup
Psychological evaluation wikipedia , lookup
Psychometrics wikipedia , lookup
Cyberpsychology wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary psychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychological injury wikipedia , lookup
Occupational health psychology wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Index of psychology articles wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Process-oriented psychology wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Political psychology wikipedia , lookup
Humanistic psychology wikipedia , lookup
Indigenous psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical psychology wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
International psychology wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
History of psychology wikipedia , lookup
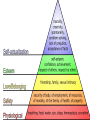
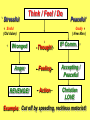
Myers’ Psychology for AP David G. Myers Worth Publishers, © 2010 Unit 1: Psychology’s History and Approaches • What is Psychology? • Contemporary Psychology What movies have you seen with professional psychologists as characters? • kind of work done? • area of specialty? • how realistic was characterization? What is Psychology? Psychology’s Roots Prescientific Psychology • Ancient Greeks LO #1 Socrates (knowledge is innate) Plato (like Socrates, used logic & opinions) Aristotle (instead, derived principles from observation) How did each view knowledge? Psychology’s Roots Prescientific Psychology • Rene Descartes (tried to explain human functioning but with theories & opinions) • Francis Bacon (introduced science to study of human functioning) • John Locke (tabula rasa is a blank slate on which experience writes) empiricism Psychology’s Roots Psychological Science is Born, p. 4 LO #2 • Wilhelm Wundt (1879) what happened? (rte) where? (UL) how measured? (hear sound, press key) Psychology developed into three different branches, or schools of thought • structuralism (structural elements) • functionalism (functions) • behaviorism (observable behavior) Psychology’s Roots Thinking About the Mind’s STRUCTURE (1890s) • Edward Titchener Structuralism • what was it? • method? introspection Psychology’s Roots Thinking About the Mind’s FUNCTION (1890s) • William James (different from Titchener how?) functionalism Mary Calkins (3 facts) Margaret Floy Washburn experimental psychology - Unit 1 Pop Quiz (get a piece of paper) A test of how you react to unexpected situations • Q#1: What did you experience when you learned of the “pop” quiz? • Q#2: Which thoughts and emotions were helpful toward performance? harmful? • Q#3: What steps might you take to overcome anxiety when faced with unexpected situations? Exercise: Psychologist as Scientist (p. 6) List three adjectives that describe a typical scientist. List three adjectives that describe a typical psychologist. Science: Where is Psychology? art chemistry ___1_________2_________3_________4_________5_________6_________7___ philosophy physics Psychological Science Develops (1920s) LO #3 • Sigmund Freud (childhood experiences and unconscious thought processes affect behavior) sex violence Psychological Science Develops (1960s) • Behaviorism John B. Watson B.F. Skinner (reinforcement theory [M&Ms]) “study of observable behavior” fidgets + GET something REMOVE something “you be the parent” (e.g., chores, homework, curfew, etc.) Behavior Encouraged Stimulus presented + (get) Stimulus removed or withheld – (remove) Behavior Suppressed Psychological Science Develops 1960s • Humanistic psychology Carl Rogers (environmental influences, need for love and acceptance) ** hypocrisy of humanism at UWO ** Abraham Maslow (hierarchy of needs) Role Play humanistic counselor (person-centered) and client Psychological Science Develops 1960s • Cognitive Neuroscience (study of brain functioning) examples . . . and my personal favorite . . . cognitive-behavioral theory 1 Stressful Think / Feel / Do Sinful (Old Adam) Godly 6 ( New Man ) 5 3 4 Peaceful 8th Comm. Wronged Thought Anger Feeling Accepting / Peaceful REVENGE! Action Christian LOVE 7 Example: Cut off by speeding, reckless motorist! 2 Assignment: In the next 24 hours, recall two occurrences when you recognize and then intentionally restructure your emotional response to a cognitive event. Prepare to share one in class. Psychological Science Develops • Psychology, p. 7 behavior (give four examples) mental processes (list five) science (describe the scientific process) Contemporary Psychology Psychology’s Biggest Question LO #4 • Nature-Nurture Issue biology vs. experience history • Greeks • Rene Descartes • Charles Darwin natural selection 1. Count off by 6. 2. 1’s, 2’s, etc., group up by number. 3. In two minutes, prepare a 30-second group response for your debate topic on p. 9. LO #5 Psychology’s Three Main Levels of Analysis • Levels of Analysis, p. 10 biological – psychological – social-cultural – • Together, they form an integrated biopsychosocial approach Psychology’s Three Main Levels of Analysis Psychology’s Three Main Levels of Analysis Psychology’s Three Main Levels of Analysis Psychology’s Three Main Levels of Analysis question on bottom p. 11 Psychological Approaches/Perspectives biological • how observable responses are acquired and changed evolutionary • how behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures psychodynamic • how the body and brain work to create emotions, memories, and sensory experiences behavioral cognitive • how behavior springs from unconscious drives and conflicts humanistic • how we encode, process, store and retrieve information social-cultural • how we meet our needs for love and acceptance, and achieve self-fulfillment • how the natural selection of traits promoted the survival of genes LO #6 Psychology’s Subfields • psychometrics • difference between basic and applied research? basic research biological psychology • investigates persistent traits developmental psychology • studies changing abilities throughout the life span educational psychology • explores how we view and affect one another personality psychology • studies influences on teaching and learning social psychology • explores link between brain and behavior applied research industrial/organizational psychology human factors psychology counseling psychology clinical psychology psychiatry • helps people cope with adjustments, challenges, and crises • used in the workplace to help companies select and train employees • medical doctors who may prescribe drugs in treatment • assesses and treats mental, emotional, and behavior disorders • focuses on interaction of people, machines, and physical environments Unit 1 Conclusion • Organize groups, assign theoretical orientation and discuss case study (today) • Groups of 3-4: In less than two minutes: 1) overview assigned theory, 2) explain case study behavior, and 3) describe likely treatment plan for client (Monday) • Competition Review (Tuesday) • Unit 1 Test (Wednesday) • Review the Test / Intro. Unit 2 (Thursday) Video: Vol. 1, DVD2, Psychological Disorders #2 Postpartum Psychosis: The Case of Andrea Yates (7:00) Set 5 Behavior of Andrea Yates (p. 9) Biological / Neuroscience – Behaviorism – Humanistic psychology – Evolutionary psychology – Psychoanalysis / psychodynamic – Developmental psychology – Cognitive psychology – Set 6 Behavior of Andrea Yates (p. 9) Biological / Neuroscience – Behaviorism – Humanistic psychology – Evolutionary psychology – Psychodynamic psychology – Developmental psychology – Cognitive psychology – Colossians 2:8 See to it that no one takes you captive through hollow and deceptive philosophy, which depends on human tradition and the basic principles of this world rather than on Christ. http://www.youtube.com/watch_popup?v=WUQYJ77qa50