* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chap 11 Sect 1 Notes Atomic Theory
Nuclear binding energy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Low-energy electron diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Geiger–Marsden experiment wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
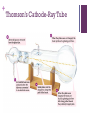
+ ATOMIC THEORY + Democritus Atom He was said to be the first step toward the current atomic theory. Hypothesized all matter is composed of tiny particles made of a single material Claimed atoms are always moving Form new substances by joining together + According forever. to him, atoms cannot be divided The object will become so small and invisible that you cannot divide it any further. He said that these indivisible, invisible particles are ATOMS. The word atom means “uncuttable”. + Aristotle Believed there was “no smallest part of matter” Substances were made up of fire, air, earth, and water + John Dalton He is best known for his work in the development of modern atomic theory. + 5 POINTS of Dalton’s Theory All matter consists of tiny particles called atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided, or destroyed. All atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties. The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element. + Compounds are formed by a combination of two or more different kinds of atoms. Compounds are pure substances. They can’t be separated into elements by phase changes because the atoms of different elements are bonded to one another and are not easily separated from one another. A chemical reaction results in a rearrangement of atoms. + J. J. Thomson Discovered of electron Discovered of isotopes Proposed Model the Plum Pudding + Thomson’s Cathode-Ray Tube + PLUM PUDDING MODEL •Also known as the “Chocolate Chip Cookie or Blueberry Muffin Model.” •Atom is composed of electrons surrounded by a “soup” of positive charge to balance the electron’s negative charge, like negativelycharged “plums” surrounded by positively-charged “pudding”. + •Sometimes visualized as having a cloud of positive charge •Electrons were free to rotate within the cloud of positive substance. + Ernest Rutherford •Discovered that atoms have their positive charge concentrated in a very small nucleus. + Gold Foil Experiment + •The results of the experiment demonstrated the existence of the atomic nucleus. + Large amount of the atom’s mass is concentrated into a very small core. Outside of this “central charge”, he proposed that the atom was mostly empty space. + Bohr’s Model also known as the planetary model neutrons and protons are in the nucleus while the electrons are orbiting the nucleus electrons are able to jump from one orbit to another + Electron Cloud Model consists of a dense nucleus composed of protons and neutrons surrounded by electrons that exist in different clouds at the various energy levels. Erwin Schrodinger and Werner Heisenburg explained where the electrons would most likely be found in the regions or clouds.