* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
ALICE experiment wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
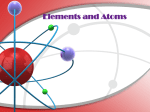
- - Positively charge particle Negatively charge particle - + Mesons + 1947 - + + - • Atoms are made out of three basic particles : 1. Protons – carry a positive charge (Ernest Rutherford discovered the proton in 1911) 2. Neutrons – carry no charge (James Chadwick contributed in the discovery of the neutron in 1932) 3. Electrons – carry a negative charge and circle the nucleus (J. J Thomson discovered the electron in 1897 ) • Protons and neutrons are made up of smaller particles called quarks. • Quarks are held to each other by particles, scientists called it gluons • Mass of 1 proton = mass of 1836 electrons • Neutrons and protons have almost the same mass • Atoms always have as many electrons as protons • Atoms usually have about as many neutrons as protons e.g. Hydrogen (1 proton, 1 electron, 0 neutron) ; Helium (2 proton, 2 electron, 2 neutron) ; Carbon ( 6 proton, 6 electron, 6 neutron). • Add a proton makes a new kind of atom • Adding a neutron makes an isotope (Greek isos = equal, tópos = site, place) of that atom, a heavier version of that atom. Isotope are any of the different types of atoms (Nuclides) of the same chemical element each having different atomic mass (mass number)