* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 06 Motor Systems
Psychologist wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
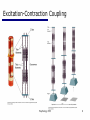
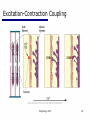
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Electromyography wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
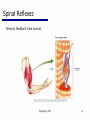
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical psychology wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Trans-species psychology wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
International psychology wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
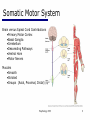
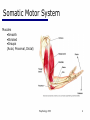
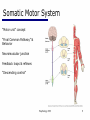
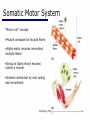
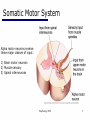
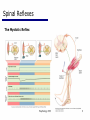
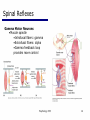
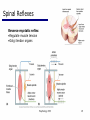
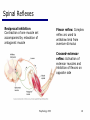
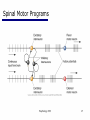
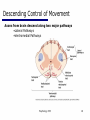
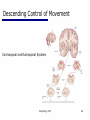
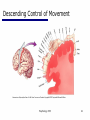
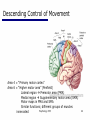
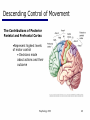
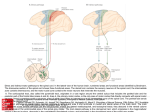
06 The Motor System Psychology 355 General Overview • • • • • • • Somatic Motor System Muscles and Motor Neurons Excitation-Contraction Coupling Spinal Reflexes Spinal Motor Programs Descending Control of Movement Diseases Affecting the Motor System Psychology 355 2 Somatic Motor System Brain versus Spinal Cord Contributions •Primary Motor Cortex •Basal Ganglia •Cerebellum •Descending Pathways •Ventral Horn •Motor Nerves Muscles •Smooth •Striated •Groups (Axial, Proximal, Distal) Psychology 355 3 Somatic Motor System Muscles •Smooth •Striated •Groups (Axial, Proximal, Distal) Psychology 355 4 Somatic Motor System “Motor unit” concept “Final Common Pathway” & Behavior Neuromuscular junction Feedback loops & reflexes “Descending control” Psychology 355 5 Somatic Motor System “Motor unit” concept •Muscle composed of muscle fibers •Alpha motor neurons innervates multiple fibers •Group of alpha motor neurons control a muscle •Graded contraction by rate coding and recruitment. Psychology 355 6 Somatic Motor System Alpha motor neurons receive three major classes of input: 1) Brain motor neurons 2) Muscle sensory 3) Spinal interneurons Psychology 355 7 Excitation-Contraction Coupling Muscle contraction •Alpha motor neurons release Ach •ACh produces large EPSP in muscle fibers (via nicotinic Ach receptors •EPSP evokes action potential •Action potential (excitation) triggers Ca2+ release, leads to fiber contraction •Relaxation, Ca2+ levels lowered by organelle reuptake Psychology 355 8 Excitation-Contraction Coupling Psychology 355 9 Excitation-Contraction Coupling Psychology 355 10 Spinal Reflexes Sensory feedback from muscle Psychology 355 11 Spinal Reflexes The Myotatic Reflex •Stretch reflex: Muscle pulled tendency to pull back •Feedback loop •Discharge rate of sensory axons: Related to muscle length •Monosynaptic •Example: knee-jerk reflex Psychology 355 12 Spinal Reflexes The Myotatic Reflex Psychology 355 13 Spinal Reflexes Gamma Motor Neurons •Muscle spindle •Intrafusal fibers: gamma •Extrafusal fibers: alpha •Gamma feedback loop provides more control Psychology 355 14 Spinal Reflexes Reverse myotatic reflex •Regulate muscle tension •Golgi tendon organs Psychology 355 15 Spinal Reflexes Reciprocal inhibition Contraction of one muscle set accompanied by relaxation of antagonist muscle Flexor reflex: Complex reflex arc used to withdraw limb from aversive stimulus Crossed-extensor reflex: Activation of extensor muscles and inhibition of flexors on opposite side Psychology 355 16 Spinal Motor Programs Psychology 355 17 Descending Control of Movement The brain influences activity of the spinal cord Voluntary movements Hierarchy of controls Highest level: Strategy Middle level: Tactics Lowest level: Execution Sensorimotor system Sensory information: Used by motor system Psychology 355 18 Descending Control of Movement Axons from brain descend along two major pathways •Lateral Pathways •Ventromedial Pathways Psychology 355 19 Descending Control of Movement Corticospinal and Rubrospinal Systems Psychology 355 20 Descending Control of Movement Psychology 355 21 Descending Control of Movement Area 4 = “Primary motor cortex” Area 6 = “Higher motor area” (Penfield) Lateral region Premotor area (PMA) Medial region Supplementary motor area (SMA) Motor maps in PMA and SMA Similar functions; different groups of muscles Psychology 355 innervated 22 Descending Control of Movement The Contributions of Posterior Parietal and Prefrontal Cortex •Represent highest levels of motor control • Decisions made about actions and their outcome Psychology 355 23 Diseases Affecting the Motor System Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) -motor neuron disease Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy -dystrophin deficit Myasthenia Gravis -autoimmune ACh receptors Parkinson’s disease - DA neurons in substantia nigra Psychology 355 24