* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Chain of Infection
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Toxoplasmosis wikipedia , lookup
Hookworm infection wikipedia , lookup
Toxocariasis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
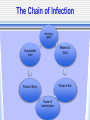
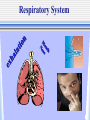
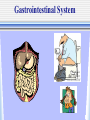
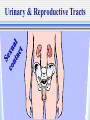
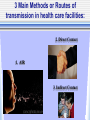
The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two things about infection: 1.How infection can be transmitted 2. How to break the infection chain There are six links in the chain of infection : The Chain of Infection Infectious agent Reservoir host Susceptible host Portal of Exit Portal of Entry Route of transmission 1st - The Infectious Agent Pathogen bacteria virus fungus 2nd - The Reservoir Host Where the microbe lives and grows. People animals Water food 3rd - The Portal of Exit -Where the microbe leaves (exits) the host Respiratory System Gastrointestinal System Urinary & Reproductive Tracts Skin Barrier/Blood Non-intact skin 4th - The Route of Transmission -HOW the pathogen gets from the reservoir host to the new host Flu virus How do I get to Mr. Smith’s lungs? 3 Main Methods or Routes of transmission in health care facilities: 2. Direct Contact 1. AIR 3. Indirect Contact th 5 - Portal of Entry The Portal of Entry is how the pathogen enters the host’s body. Usually the same as the Portal of Exit. 6th - The Susceptible Host -the person that the pathogen enters A susceptible person is someone at higher risk for developing an infection Susceptible Hosts • • • • The elderly People with low immune systems, Health care workers Infants What are ways can you think of to prevent the transmission of germs? • Power Point adapted from: • www.cte.unt.edu/health/curriculum/Chain_ of_Infection.ppt • Some images from Google Images