* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sentence Types - Mrs. Olinger's English Page
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
American Sign Language grammar wikipedia , lookup
Antisymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Relative clause wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Determiner phrase wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
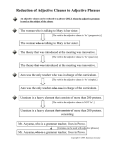
CLAUSES AND PHRASES Adjectival, adverbial, and nominal Clause vs phrase • A clause is a group of words that has as a subject and predicate. • A phrase does not. • A phrase is a group of words that lacks either a subject or a predicate. Adjective Clause • Modify nouns or pronouns • Adjective clauses tend to begin with (or these are implied) • Who, whom, whose, which, or that • When, where, why • To test for adjective clause, they usually answer these questions: • Which one? What kind? • Because they tend to begin with these relative pronouns or adverbs, they are usually dependent clauses. Where is the adjective clause? • The dog that sat in the swing wanted to be pushed. • The curly labridoodle, whose big, brown eyes pleaded for a push, waited patiently. • The man who put the dog in the swing should be punished. Adjective Phrase • Modify nouns or pronouns • Modify the same things the same way, but rather than using a clause, use a group of words (a phrase!) • Like a normal adjective, an adjective phrase can be used before the noun it is modifying (like in the first two examples above) or after the noun it is modifying (like in the last example) • Read more at http://www.grammar- monster.com/glossary/adjective_phrases.htm#IzZiSExMRUg0WpR B.99 Where is the adjective phrase? • The dog in the swing wanted to be pushed. • The curly labridoodle, with big, brown eyes, waited patiently. • The man who put the dog in the swing should be punished. Adverbial Clause—contains a subject and a verb • Modifies verbs • Answers these three questions: • How / Why? • When? • Where? • Tend to start with subordinating conjunctions so they are usually DEPENDENT! Where is the adverbial clause? • With his arms at his side, the alligator breached like a dolphin • He shot out of the water after he saw the duck. • He put on a show in a lake that has fresh water Where is the adverbial phrase? • The alligator breached like a dolphin • In three seconds he shot out of the water. • Near the middle of the lake he put on a show. Nominal Clause • Like a noun, a nominal clause names a person, place, thing, or idea. A nominal clause may function in a sentence as any of the following: Subject Subject Complement Appositive Object of a preposition Direct object Indirect object Examples • During Halloween you can dress like whomever you want. • They argue about how they will pay the bill. • I don’t know who stole my grill.