* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download the earth`s interior
Survey
Document related concepts
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
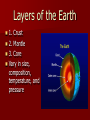
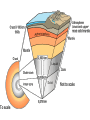
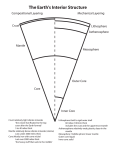
THE EARTH’S INTERIOR Layers of the Earth 1. Crust 2. Mantle 3. Core Vary in size, composition, temperature, and pressure The Crust The layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer surface. Basalt makes up the oceanic crust Granite makes up the continental crust. 5-40 km thick Temperature is 57° - The Mantle The layer of hot, solid material between Earth’s crust and core About 40 kilometers below surface 2,867 km thick Temperature is 2190° C Lithosphere – a rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust Asthenosphere – the soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats The Core Located below mantle 3,480 km total thickness Made mostly of iron and nickel 2 layers: outer core- liquid rock, 2266 km thick, 5624° C inner core- solid rock, 1216 km thick, 5624° C Earth’s Magnetic Field Caused by the movement of the liquid outer core Similar to the magnetic field on a Text gigantic bar magnet Convection and the Mantle I. Types of Heat Transfer • • • Radiation Conduction Convection radiation – the transfer of energy through space heat from the sun heat from a fire Conduction – heat transfer within a material or between materials that are touching convection – the transfer of heat by movement of a fluid Density -measure of how much mass there is in a volume of a substance D= M÷V convection currents – the movement of a fluid, caused by differences in temperature, that transfers heat from one part of the fluid to another