* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mantle & Crust
Survey
Document related concepts
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Provenance (geology) wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
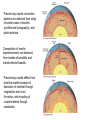
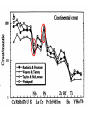
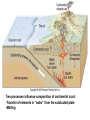
Silicate Earth • • • • • Primitive mantle Present-day mantle Crust Oceanic crust Continental crust Reservoir Volume (1027 cm3) Mass (1027g) Mass % Earth Core Mantle Crust (continental) Hydrosphere Atmosphere 1.083 0.175 0.899 0.00842 0.00137 - 5.98 1.88 4.08 0.0236 0.00141 0.000005 100 31.5 68.1 0.4 0.024 0.00009 Evidence for mantle composition: • Sampled by xenoliths, occasionally exposed by crustal deformation – Peridotite – Eclogite • Seismic velocities match both rocks • Must melt to form basaltic magma – Peridotite melting – up to about 40% – Eclogite melting – must be close to 100% 3 types of primary basaltic magma •At divergent plate margins (mid ocean ridges) – magma rises from asthenosphere decompression melting at low pressure - tholeiitic basalt •At hot spot (intra-plate volcanoes) – magma rises from deep mantle - decompression melting at high pressure - alkali basalt •At convergent plate margins (volcanic arcs) – water added to the mantle from the subducted lithosphere causes melting - flux melting - calc-alkaline basalt Present day mantle convection patterns are deduced from study of seismic wave velocities (profiles and tomography), and plate tectonics. Composition of mantle layers/reservoirs are deduced from studies of xenoliths and mantle-derived basalts. Present-day mantle differs from primitive mantle because of extraction of material through magmatism and crust formation, and recycling of crustal material through subduction. Trace elements in mantle • Primitive mantle – chondrites for refractory elements, ingenious estimates for volatile elements, mainly based on isotopic calculations • Present day mantle – – Analyze xenoliths – but these are extremely variable – Infer compositions by looking at basalts and modeling the melting process Mantle derived basalts: Mineral/melt partition or distribution coefficients – define the ratio of an element in a mineral compared with a melt at chemical equilibrium. Used to infer source composition. KDs reflect the ability of an element to enter the structure of the mineral. Ionic radius Mantle derived basalts: Mantle source of MORB – must be depleted compared to primitive mantle Mantle source of OIB – must be enriched compared to primitive mantle Mineral abundances: 39% plagioclase, 12% quartz, 12% K-feldspar, 11% pyroxene, 5% mica, 5% amphibole, 3 olivine, 5%clay, 2% carbonate, 8% other “Stack Models” Rudnick and Fountain, 1995 – first thorough study of upper and lower continental crust Based on seismic velocities, lower crust can be gabbro, granulite or amphibolite, but not eclogite Trace element estimates from: 1) Rock averages from stack models (gabbro, granite, limestone, etc.) 2) Materials that sample large areas of the crust as the result of sedimentary processes like shale and loess – North American Shale Composite (NASC) 3) Heat production – match abundances of K, U, Th Puzzle: Why is average continental crust andesitic? Where is the complementary gabbroic material? Lower crust is insufficient. Two processes influence composition of continental crust: •Transfer of elements in “water” from the subducted plate •Melting Much of continental crust was formed in subduction zones Basalts from subduction zones – island arc basalt