* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquakes
Seismic inversion wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Ionospheric dynamo region wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Seismic communication wikipedia , lookup
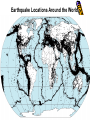
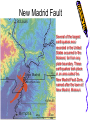
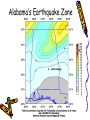
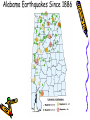
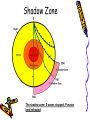
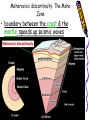
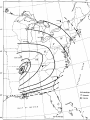
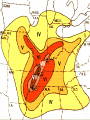
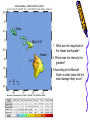
Earthquakes Chapter 8 & Then Some Write down the underlined items for your notes to study. Earthquake Zones • Earthquakes can occur near the Earth’s surface or far below the surface. • Most earthquakes occur at plate boundaries (in earthquake zones), but some happen at faults located in the middle of tectonic plates. Earthquake Locations Around the World Seismologists: Scientists who study earthquakes. – Earthquakes are caused by deformation of rock. • Plastic deformation = bending; no earthquake • Elastic deformation = breaking with earthquake Location of Earthquakes: • Seismologists use seismograms to find the epicenter of earthquakes. • Epicenter is the point on top of the Earth above the true center of an earthquake. • Earthquake Focus: • The place inside the earth where earthquakes begin. Earthquakes Boundaries & Faults: Earthquakes occur at all boundary/fault types. Earthquakes in Alabama?! Surely, you’re kidding? How? Why? The New Madrid Fault • If there is no plate boundary in the middle of the United States, why do these earthquakes take place? • Geologists are beginning to understand the answer. The New Madrid Fault Zone is part of an ancient plate boundary. In this area, the North American Plate tried to form a divergent plate boundary about 500 million years ago. The splitting stopped before new plates could form. • The faults in the New Madrid Zone are remnants of this old event. Earthquakes occur because the North American Plate is still "settling down". The faults in the New Madrid Zone do not reach the Earth’s surface. They are buried beneath thousands of feet of rock and sediment deposited by the Mississippi River. Geologists have located them by looking at the patterns of earthquakes in the zone. New Madrid Fault Several of the largest earthquakes ever recorded in the United States occurred in the Midwest, far from any plate boundary. These earthquakes took place in an area called the New Madrid Fault Zone, named after the town of New Madrid, Missouri. New Madrid Fault • Over a three-month period in the winter of 1811 to 1812, the New Madrid Fault Zone was struck by three huge earthquakes estimated to be greater than magnitude 8.0 . • The New Madrid Fault is what causes Alabama to experience earthquakes. Alabama’s Earthquake Zone Alabama Earthquakes Since 1886 Earthquakes in Alabama • The last earthquake to occur in Alabama was on September 11, 2009, 35 miles south of Tuscaloosa. – It measured a 2.3 on the Richter scale. (A little stronger than the one crazed LSU fans caused in October 9,1988, when they defeated Auburn 7-6 for the SEC title. 80,000 people jumping up & down created surface waves, triggering an earthquake. Imagine that many people jumping up & down on a trampoline.) • This was not a very strong earthquake, but it was recorded by a seismograph, an instrument used to measure earthquakes. Earthquake Energy: Just How Strong Was It Anyway? Earthquake Energy=Seismic Energy How do Earthquake Waves Travel? • Energy released from moving plates & faults travels through the Earth as waves. • Waves travel at different speeds & in different ways, depending on what kind of material they are moving through. Earthquake Energy This energy is called seismic energy and is measured in seismic waves: – Two types of seismic waves: • body waves • surface waves Body Waves: waves that travel through the Earth’s interior • There are two types of body waves: – P-waves – S-waves P and S wave comparison P-waves: primary waves or pressure waves • travel through solid, liquids and gases • fastest waves (travel 5-8 km/h), arrive first & are first ones to be detected • P-waves cause rock to squeeze and stretch. Imagine a slinky! P-Waves S-waves: secondary waves • second fastest waves; 2nd to arrive; shear waves • slower than P-waves; travel 3-5 km/h • S-waves move rock from side to side. • S-waves can’t travel through parts of the Earth that are completely liquid. S-Waves Surface Waves • move along the surface of the Earth • can move up, down & around or side to side • Surface waves move the slowest & cause the most destruction. – Think about it? Where do most people live: on the Earth’s crust or in it? Shouldn’t these waves be the most destructive since they occur where there is more stuff to destroy? Surface Waves Seismic Wave Arrival • First- P-waves • Second- S-waves • Third- Surface Waves The area of the Earth that does not receive seismic energy is called the Shadow Zone. Shadow Zone The shadow zone: S waves stopped; P waves bent/refracted Mohorovicic discontinuity: The Moho Zone • boundary between the crust & the mantle: speeds up seismic waves Quiz • • • • • • 1. Most Earthquakes occur along ________________. 2. The first seismic waves to arrive are______________. 3. The second seismic waves to arrive are _____________. 4. The last seismic waves to arrive are_______________. 5. Which seismic waves travel the fastest?___________ 6. Which type of seismic wave can move through a solid, liquid or a gas?________________ • 7. Which seismic wave cannot travel through material that is completely liquid?______________ • 8. Which seismic waves are the slowest and the most destructive?_______________ Measuring Earthquakes Seismographs & Seismograms Wait aren’t those the same? Measuring Earthquakes • Seismographs: instruments used to sense earthquakes – seismogram: tracing of earthquake movement made by seismograph • Seismologists use seismograms to locate earthquakes. Picture of a Seismograph Time and Location of Earthquakes • Seismologists use seismograms to find the epicenter of earthquakes: – the point on top of the Earth above the true center of an earthquake which is called the focus—it’s inside the Earth. (Also called the hypocenter.) Seismograms Measuring Earthquakes • Earthquakes are defined by their strength and depth, which is measured at the place the earthquake occurs. • 2 Scales are used to rank the quakes: – Richter Scale—measures magnitude – Mercalli Scale—measures intensity Earthquake strength & intensity • Richter scale: measures magnitude (think strength) of ground motion on a scale of 2.0-8.0 (numbers) • Mercalli scale: measures degree to which an earthquake is felt by people & amount of damage caused, which is known as intensity – Scale of I-XII (Roman Numerals) Magnitude Effects 2.0 (2-2.9 very minor) Only felt by seismograph 3.0 (3-3.9, minor) Felt at epicenter 4.0 (4-4.9 light) Felt by most people in area 5.0 (5-5.9, moderate) Damage at epicenter 6.0 (6-6.9, strong) Widespread damage 7.0 (7-7.9 major) Great, widespread damage 8.0 or higher (8 & up, great) Catastrophic destruction Reading Richter Scale Maps Reading Mercalli Scale Maps Seismograph • • • A seismograph is an instrument used by scientists to measure earthquakes. Seismologists who study earthquakes can determine when an earthquake started by noting the arrival times of P-waves and S-waves. A seismograph records vibrations in the Earth and determines the strength and location of an earthquake. Chinese Seismograph Ancient Chinese Seismograph. The ball would drop from the dragon to the frog. It told the people from which direction the earthquake came. Seismograms 0 1 2 3 Time in Minutes 4 5 6 7 1. How many minutes did it take for the P-Waves to arrive? 2. How many minutes did it take for the S-waves to arrive? 3. How long did the surface waves last? 8 IV Oahu Maui V-VI 1. What was the magnitude of the Hawaii earthquake? Hawaii 6.7 VII VI V 2. Where was the intensity the greatest? 3.According to the Mercalli Scale on what island did the most damage likely occur? Mercalli Intensity Scale 1. What is the intensity at Monterey? Smith 2. What is the intensity at the epicenter? 3. What is the intensity at San Jose? 4. What is the intensity at Santa Cruz? 5. What is the intensity at Smith?