* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
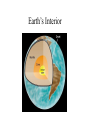
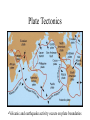
Earth Chapter 7 Basic Properties • Terrestrial planet (the original!) • Composition – rocky (heavy elements: oxygen, silicon, iron) – very different from sun and Jovian planets • Orbit – nearly circular • Climate – Not too hot, not too cold: JUST RIGHT! • only planet with liquid water • water necessary for life Earth: The Water Planet Earth’s Interior Probing Earth’s Interior • Earthquakes – Seismic waves – Penetrate interior – Path depends on material properties QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncomp resse d) de co mpres sor a re ne eded to see this picture . Earth’s Interior • Temperature increases toward center – Rock melts QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. • Differentiation – Interior is molten – Heavy elements sink; light elements float • Core is molten iron (density 8 gm/cm3) • Mantle is partially melted (density 5 gm/cm3) • Crust is solid (density 3 gm/cm3) • Crust Floats on Mantle Earth’s Crust Plate Tectonics QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 70 million yrs ago 200 million yrs ago QuickTime™ and a GIF decompressor are needed to see this picture. Qu ic kTi me™ a nd a TIFF (U nc omp res se d) de co mpre ss or are n ee de d to se e thi s p i cture . 500 million yrs ago 700 million yrs ago Plate Tectonics •Volcanic and earthquake activity occurs on plate boundaries Mantle Convection • • • • Heat escapes core; heats mantle Hot mantle rises Convection Cold mantle sinks Convection flow carries crust sideways Subduction Rift Zone Subduction QuickTi me™ and a TIFF (U ncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Rift and Subduction Zones Slip Fault Rift Zone Subduction Zone QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Rift Zone • Occurs when crust is split apart QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Subduction • Occurs when plates pushed together Pacific Northwest QuickTime™ and a TI FF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed t o see this picture. Quic kTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompress ed) dec ompres sor are needed to s ee this pic ture. Mt. St. Helens Eruption QuickTime™ and a TI FF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed t o see this picture. QuickTi me™ and a TIFF (U ncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Uplift: Building Mountain Ranges Qui ckTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompr essor ar e needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TI FF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this pict ure. Slip Fault • Occurs where plates slip sideways San Andreas Fault Hawaiian Island Chain • Line of successive volcanoes; middle of plate • Produced when plate travels over “hot spot” Quick Time™ and a TIFF (Uncompress ed) decompress or are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TI FF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this pict ure. Repaving the Earth • Ocean floor renewed in few 100 million yrs • Continents last longer – Surface features erased by erosion (water and wind) • Evidence of craters erased in time – Oldest rocks on earth about 3.8 billion yrs old • Radioactive dating Volcanoes are usually found in places where: A. the low pressure of the atmosphere pulls the lava/magma to the surface. B. earthquakes occur from oceanic plates colliding with continental plates. C. deep-rooted mountains have cracked Earth’s crust. D. Earth’s rotation has caused weak spots in its crust. The change in position of the continents over time is primarily caused by A. B. C. D. continental plates floating on the ocean. mantle material circulating inside Earth. Earth’s slow shrinking as it cools. global wind patterns and sustained ocean currents. Earth’s Atmosphere • Composition – – – – Mostly nitrogen, N2 (78%) Some oxygen, O2 (21%) A little water, H2O Teeny, tiny bit of carbon dioxide CO2 • Atmospheric Pressure – 14.7 pounds per square inch (1 bar) – Produced by weight of atmosphere above us Atmospheric Protection • Ozone, O3 – Ozone absorbs ultraviolet light – Protects us from sunburn – Ozone destroyed by chlorine • NOTE: Ozone destruction NOT same problem as global warming! Ozone and CFCs QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 2000 Ozone hole Over Antarctica QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Change in CFC-11 Last 20+ years Chemical Evolution of Atmosphere • Original Atmosphere – Mostly carbon dioxide, CO2 • Current Atmosphere – Mostly nitrogen, N2 – Oxygen disappears (a few 1000 yrs) if not replenished (oxygen produced by plants) • Where did CO2 go? – Bound in rocks (like limestone, calcium carbonate, CaCO3) • Where did nitrogen and water come from? – Volcanic activity releases N2 and water, H20 – Comets falling on Earth release water Greenhouse Effect • Sunlight absorbed by ground • Heat emitted using infrared light • Infrared light trapped by gasses in Earth’s atmosphere – Greenhouse gasses: • Carbon Dioxide (CO2) • Water (H2O) • Heat cannot escape • Earth’s surface gets hotter – about 23 degrees C (40 degrees F) Global Warming QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Quic kTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompress ed) dec ompres sor are needed to see this pic ture. QuickT im e™an d aTI FF( Un compr essed) decom p r essor a re n eede d t oseet hispictur e. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncomp resse d) de com press or are nee ded to s ee this picture. Atmospheric Protection • Meteors (“shooting stars”) – Small rocks melt/burn up before hitting surface – Larger objects can get through QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 1833 Leonid Storm 1998 Leonids QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. 1997 Leonids Seen by MSX Meteor Showers Causes of Meteor Showers QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Peekskill Meteorite QuickTime™ and a YUV420 codec decompressor are needed to see this picture. 1992 Perils from Space QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a TIFF (Uncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTi me™ and a TIFF (U ncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. Effects of Impacts • Where are the craters on Earth? – erased by geologic activity • volcanoes, earthquakes, plate tectonics – erased by erosion • weather, rain, wind • Evidence for impacts? QuickTi me™ and a TIFF (U ncompressed) decompressor are needed to see this picture. – some craters still exist (Meteor Crater, AZ) – geologic evidence of old craters – occasional impacts today • Effects of impacts? – global climate changes • mass extinctions? (dinosaurs) – water in oceans? Q ui ck Ti m e ™ an d a T I FF ( U nc om p r es se d) de co m pr e ss or ar e n ee de d t o se e t hi s