* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STI`s
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Management of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
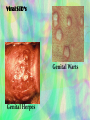
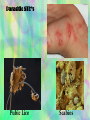
Sexually Transmitted Infections Mr. Springer 8th Grade Health What Is An STI? Why Is STI Education Important? • STI- infection spread from person to person through sexual contact *Each year, one-quarter of all new cases of STI’s occur among 15-19 year-olds. What Is An STI? Why Is STI Education Important? • Up to 75 percent of sexually active women and men will get an STI of some kind. Planned Parenthood 2007. • Medically, an STI is an infection first, after it causes symptoms, the infection becomes a disease. An STD - sexually transmitted disease - is an infection that has symptoms. What You Should Know About STI’s 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Most STI’s are spread only through sexual contact You cannot tell if someone has an STI by his or her appearance A person with an STI may have no symptoms Many STI’s can be treated, but early diagnosis is vital Because treatment for STI’s vary, they must be accurately identified STI’s can recur because the body does not build up immunity to them STI’s are serious diseases that can cause sterility, blindness, deafness, insanity, and death Best Method Of Preventing STI Infection? • Abstinence! – When you practice abstinence, you avoid serious consequences of contracting an STI – This prevention is critical because STI’s differ from other communicable diseases in 2 ways: – There are no vaccines for any STI’s except hepatitis B – You body cannot build immunity to STI’s Responsible Communication • Responsible Behavior! – Choose your friends carefully – They should share your values and support your decision about practicing sexual abstinence – Group activities remove pressure for sexual activity – Know your limits and communicate them to your date before you go out – Say no through your words & actions – Seek advice from a trusted adult on handling difficult situations 3 Causes Of STI’s 1. Parasites- can be large enough to see, can be cured with medication 2. Bacteria- are too small to see, can be cured with antibiotics 3. Viruses- are so small, they may even go through condoms, there are no cures for viral STI’s How STI’s Enter The Body • STI’s enter the body through wet, warm mucous linings at body openings. – Most common entry sites are: • • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Penis Vagina Anus Mouth Open Sores STI Warning Signs • Persons with STI’s sometimes have symptoms like a: – 1. Sore – 2. Rash – 3. Painful Urination – 4. Discharge – 5. Swollen Lymph Nodes In Groin *Often there are no warning signs, many people who have STI don’t even know it! Common Sexually Transmitted Infections Chlamydia Chlamydia (bacteria) – – – Symptoms: burning during urination, irritation of genitals, discharge, females may have mild or no symptoms Treatment: antibiotics What Could Happen: sterility from scarring of reproductive organs, infections of developing fetus in pregnant women Gonorrhea Gonorrhea (bacteria) – Symptoms: discharge, swollen lymph nodes in the groin, burning during urination, females may have mild or no symptoms – Treatment: Antibiotics, but some strains or bacteria are drug resistant – What Could Happen: sterility, permanent damage to joints and body organs, infection of developing fetus in pregnant women Genital Herpes Genital Herpes (HSV-2, Virus) – Symptoms: painful, itchy blisters in genital area, fever, burning when urinating during an outbreak – Treatment: no cure, medication care relieve symptoms – What Could Happen: increased risk of HIV infection, brain damage or death of newborns of infected mothers Genital Warts Genital Warts (HPV - Virus) – Symptoms: painless warts in the genital area 3 weeks to 6 months after exposure to infected person – Treatment: topical medication, freezing or surgery to remove warts – What Could Happen: cancer of reproductive system, urinary blockage in males, cervical cancer in females, infection of newborns during birth Syphilis Syphilis (bacteria) – Symptoms: red sores in genital area; body rash; flu-like symptoms; symptoms may disappear though disease is still active – Treatment: antibiotics – What Could Happen: increased risk of HIV infection; damage to cardiovascular system, kidneys, and nervous system; blindness; insanity; death; birth defects in developing fetus of pregnant woman Pelvic Inflammatory Disease PID (females only) (bacteria) – Symptoms: foul-smelling discharge; tenderness in abdomen; backache; fever; vomiting; heavy menstrual periods – Treatment: antibiotics – What Could Happen: sterility from scarring of reproductive organs; constant pelvic pain Hepatitis B Hepatitis B (HBV Virus) – Symptoms: loss of appetitie; nausea; yellowing of the skin; joint pain – Treatment: prevented by vaccination; no treatment otherwise – What Could Happen: liver damage; liver cancer; ;infection of the developing fetus in pregnant women Pubic Lice Pubic Lice (Parasite) – Symptoms: itching, presence of lice and eggs in pubic hair – Treatment: medicated soaps, washing all bed linens and clothes – What Could Happen: no lasting effects Viral STD’s Genital Warts Genital Herpes Parasitic STD’s Pubic Lice Scabies