* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download X - kendricknovak
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
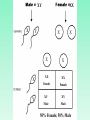
Welcome What is a dihybrid cross? Agenda • Quiz • Sex Linked Traits • Mutations Sex Determination • Thomas Hunt Morgan – studied fruit flies in the early 1900’s Sex Determination • Observed that one pair of chromosomes was different between males and females – Large one named “X” chromosome – Smaller one named “Y” chromosome – XX = female; XY = male XY X XX Y X Y X X X X XX XX Female Female XY XY Male Male 50% Female; 50% Male Sex Linkage • Sex Linkage: the presence of a gene on a sex chromosome (X or Y) Sex Linkage • X-linked genes: genes found on the X chromosome – X chromosome carries more genes • Y-linked genes: genes found on the Y chromosome Fruit Fly Eye Color • Fruit flies normally have red eyes • A few males have white eyes • Red is dominant; white is recessive Morgan’s Fruit Fly Experiments • Red-eyed female (XRXR) x White-eyed male (XrY) XR XRX r XR XRXr Xr F1 generation – all red-eyed XRY Y RESULTS: XRY Morgan’s Fruit Fly Experiments • Red-eyed female (XRXr) x Red-eyed male (XRY) XR Xr XRX R XRXr F2 generation – 3 red-eyed and 1 white-eyed XRY XrY ** all white-eyed where males…why? XR Y RESULTS: Morgan’s Conclusions • Gene for eye color is carried on the X chromosome = eye color is an X-linked trait • Y chromosome does not carry a gene for eye color • Red-eyed = XRXR, XRXr , XRY • White-eyed = XrXr, XrY In humans colorblindness (b) is an example of a sex-linked recessive trait. A male with colorblindness marries a female who is not colorblind but carries the (b) allele. Using a Punnett square, determine the genotypic and phenotypic probabilities for their potential offspring. Welcome What is an X-Linked trait? Agenda • Review sex linked traits • Mutations • Movie Review In fruit flies red eye color (R) is dominant to white eyes (r). In a cross between two flies, 50% of the male and 50% of the female offspring had red eyes. The other half of the males and females had white eyes. What are the phenotype, and all possible genotypes, of the offspring? Worksheet Linkage Groups • 2 or more genes that are on the same chromosome are “linked” • Linked genes tend to be inherited together More Fruit Fly Experiment • Gray, long-winged (GGLL) x black, short-winged (ggll) • F1 generation = all heterozygous gray, long-winged (GgLl) Morgan’s Fruit Fly Experiment • Cross F1 flies: GgLl x GgLl • F2 generation – If alleles on different chromosomes, they assort independently and get a 9:3:3:1 ratio – If alleles on same chromosome, get 3 gray, longwinged: 1 black, short-winged ratio – Morgan saw roughly the 3:1 ratio Morgan’s Fruit Fly Experiment • Unexpected results – Some gray, short-winged (Ggll) – Some black, long-winged (ggLl) Morgan’s Fruit Fly Experiment • How were these alleles separated? – Alleles were rearranged through crossing-over during meiosis • Genes that are farther apart are more likely to be separated by crossovers Chromosome Mapping • Chromosome Map: diagram that shows the possible genes on a chromosome • Made using crossing-over data Chromosome Mapping • The percentage of crossing-over between the genes for 2 traits is equal to the distance between them on a chromosome • This distance is measured in map units