* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download geneticengineering fall 2012 genetics unit
Survey
Document related concepts
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
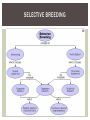
WHAT IS GENETIC ENGINEERING? Genetic engineering is the manipulation of an organism’s genes to create a desired characteristic. AKA= changing an organism’s DNA WHAT IS GENETIC ENGINEERING IS USED FOR? Scientists uses genetic engineering to knock out certain genes from an organism in order to observe the effects and mutations caused by those genes. With the mapping of the human genome and the genomes of other important animals and plants, scientists have been able to manipulate the genes of other organisms in order to produce beneficial products for humans. T YPES OF GENETIC ENGINEERING Selective Breeding: Allowing only those animals with the desired charcteristics to reproduce the next generation. Ex. Nearly all domestic animals SELECTIVE BREEDING T YPES OF GENETIC ENGINEERING Hybridization The Crossing of dissimilar individuals to bring together the best of both organisms. Hybrids are usually hardier than either parent. Labradoodle INBREEDING The continued breeding of individuals with similar charcteristics 1. Breeders use this to maintain desired characteristics of a line of organisms. 2. Problems result b/c there is always a chance that a cross between 2 individuals will bring together 2 recessive alleles. Ex. Blindness, jointdeformities. GENETICALLY ENGINEERED FOODS Just kidding. Farmers have been producing foods that have been genetically altered to be more nutritious, delicious, resistant to harmful pesticides and have the ability to repel pests. Harmful long term effects have yet to be seen in consumers. CREATING YOUR OWN CHILD Scientists and doctors have been able to genetically plan certain characteristics in embryos. Since the mapping of the human genome, finding specific genes and their qualities has become much simpler. Parents now have an opportunity to “design” their ideal child. CONTROVERSIES Consumers of the genetically engineered foods are worried about the adverse effects that the foods might have on them. Since this is a new technology, there hasn’t been a lot of time to examine the long term effects of these new foods. Some consider it inorganic. DNA FINGERPRINTING 1.Samples of organism’s DNA is exposed to restriction enzyme which cuts it into pieces 2.DNA is run through an electrophoresis machine using gels 3.Since DNA is cut at certain sequences, each piece is a different length and has a different weight 4.Pieces that are heavier stay at the top of the gel, while lighter will “run” to the bottom of the gel DNA FINGERPRINTING 5. Every person is genetically different so their gels would appear different A. identical twins have identical DNA fingerprints B. people who are closely related have similar DNA markers DNA FINGERPRINTING APPLICATIONS A. can be used to identify or eliminate suspects B. can be used to determine paternity of a child C. can be used to identify a deceased person