* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendel`s Principle of Independent Assortment
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
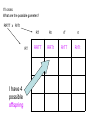
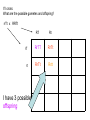
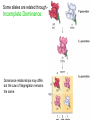
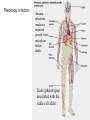
Dihybrid Crosses looking at 2 traits Mendel’s dihybrid crosses: 1. Mendel also performed crosses involving two pairs of traits, e.g., seed shape (smooth vs. wrinkled) and color (yellow vs. green). 2. If alleles sort independently, four possible phenotypes (2n) appear in the F2 generation in a 9:3:3:1 ratio. “Mendel’s Principle of Independent Assortment”: Alleles for different traits assort independently of one another. Modern formulation of independent assortment: Genes on different chromosomes behave independently in gamete production. The Independent Alignment of Different Pairs of Homologous Chromosomes At Meiosis Accounts for the Principle of Independent Assortment The alignment of one pair of homologs is independent of any other.Assortment: The Principle of Independent assortment of one pair of genes into gametes is independent of the assortment of another pair of genes. Possible Gametes: To determine the number of different gametes a parent can have use the FOIL method. RREE RE RE RE RE All gametes are RE Possible Gametes: To determine the number of different gametes a parent can have use the FOIL method. RREe Re RE RE Re You have 2 possible gametes: Re and RE Possible Gametes: To determine the number of different gametes a parent can have use the FOIL method. rrEe re rE rE re You have 2 possible gametes: rE and re How many gametes? To determine the number of different gametes a parent can have use the FOIL method. Number and kind of gametes TTYY = one TtYY = two TtYy = four TY TY and tY Ty, tY, ty, TY Possible Gametes (sperm/egg): If I cross: What are the different possible gametes for these parents?? RRTT x RrTt RT RT, Rt, rT, rt There are 4 total different gametes If I cross: What are the possible gametes? RrTt x RrTt I have 16 possible offspring 9:3:3:1 RT Rt rT rt RT RRTT RRTt RrTT RrTt Rt RRTt RRtt RrTt Rrtt rT RrTT RrTt rrTT rrTt rt RrTt Rrtt rrTt rrtt If I cross: What are the possible gametes? RRTT x RrTt RT I have 4 possible offspring RT Rt rT rt RRTT RRTt RrTT RrTt If I cross: What are the possible gametes and offspring? rrTt x RRTt RT Rt rT RrTT RrTt rt RrTt Rrtt I have 3 possible offspring Why Did Mendel Conclude That The Inheritance of one Trait is Independent of Another? Phenotype Ratio: 9 yellow/smooth 3 yellow/wrinkled 3 green/smooth 1 green/wrinkled Because it’s the only way to explain the pattern of inheritance. What Works for Peas Also Works for Humans Consider a cross between parents heterozygous for both deafness and albinism. This is the same 9:3:3:1 ratio seen for Mendel’s cross involving pea color and shape. Take out: Exercise: Dihybrid Crosses Complete all questions and check your answers with me. Exceptions to the rule… Some alleles are related through - Incomplete Dominance Dominance relationships may differ, but the Law of Segregation remains the same. Multiple Alleles Many genes are present in 3 or more versions (alleles) – this is known as multiple alleles. The human ABO blood group is determined by three alleles (IA, IB, and i) of a single gene. The AB phenotype (genotype IA IB) is an example of codominance Codominance The human ABO blood group illustrates another genetic phenomenon – codominance. Codominance occurs when the phenotype associated with each allele is expressed in the heterozygote. Neither allele is dominant or recessive Incomplete or Codominant? + Pleiotropy – When One Allele Influences Many Traits Examples: 1. Sickle Cell Anemia 2. Albinism Pleiotropy in Action Anemia, infections, weakness, impaired growth, liver and spleen failure, death. Traits (phenotypes) associated with the sickle cell allele. Polygenic Inheritance – when a Single Trait is influenced by many genes Examples: 1. Height 2. Hair texture 3. Skin color 4. eye color Corn Lab – Dihybrid Cross On a sheet of paper, count 200 kernels of corns and perform a chi-square analysis: Your options are: Purple, smooth Purple, wrinkled Yellow, smooth Yellow, wrinkled What ratio did Mendel see on his dihybrid corn? That is your expected ratio….