* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biotechnology Content Review
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified food wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
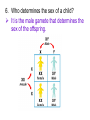
Competency Goal # 3 The learner will develop an understanding of the continuity of life and the changes of organisms over time. Part 4 1. Why should close relatives not mate? Most human disorders are inherited as rare recessive alleles. Mating with close relatives increases the chances that a recessive disorder will be inherited. 2. If a trait is sex-linked, where is the gene located? On the 23rd chromosome; most on X 3. Name sex-linked traits in humans. Red-green color blindness Hemophilia 4. Show a Punnett square of a carrier female and normal male. 5. What is a pedigree? A graphic representation of genetic inheritance 6. Who determines the sex of a child? It is the male gamete that determines the sex of the offspring. 7. What is meant by a polygenic trait? A trait that is controlled by two or more genes. Skin color, and height are examples 8. What important contribution did Charles Drew make? Improved storage for blood storage and increasing the blood blank 9. What is a karyotype? Chart of chromosome pictures enlarged and arranged in pairs 10. What can you tell by looking at the chromosomes in a karyotype? Valuable in identifying unusual chromosome numbers in cells 11. Explain how amniocentesis can be used to screen for genetic disorders. A small amount of amniotic fluid, which contains fetal tissues, is extracted and the fetal DNA is examined 12. How can gel electrophoresis be useful: Law enforcement: Matching DNA samples from crime scenes; fingerprinting Medicine: Research in developing cures for diseases 13. How can human insulin be produced using DNA technology? The human gene for insulin is inserted into a bacterial plasmid by genetic engineering techniques. Recombinant bacteria produce large quantities of insulin. 14. What is a transgenic organism? A plant or animals that contain functional recombinant DNA from an organism of a different genus Example: high protein corn, better tasting, last longer, resistance to pest and disease, increased vitamins 15. What is cloning? The process of making a genetically identical copy 16. What are the advantages and disadvantages of cloning? Advantage: Rancher and dairy farmers could clone particularly productive, healthy animals to increase yield; medical research Disadvantage: Ethical issues