* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review ch 11 Patterns of Inheritance
Survey
Document related concepts
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Sexual dimorphism wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
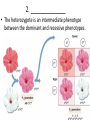
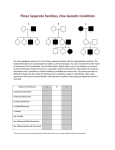
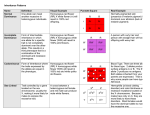
Review ch 11 Complex Patterns of Inheritance Biology Types of Inheritance you should know • • • • • • • • • Incomplete Dominance Co-dominance Multiple Alleles Epistasis Sex Determination Dosage Compensation Sex-Linked Traits Polygenic Traits Environmental Influences What type of Inheritance is shown in the following slides? • On a blank sheet of paper, write your name, class hour, and number it from #1-12. • Work with your table partner to determine the types of inheritance patterns from the following examples………-> 1. ______________ • The image shows a heterozygote both the dominant normal red blood cell and the recessive sickle cell present at the same time. • Heterozygous individuals are able to live relatively normal lives 2. ______________ • The heterozygote is an intermediate phenotype between the dominant and recessive phenotypes. 3. _________________ • Some traits exhibit many phenotypes and vary across a broad range. – – – – – Height of a person Hand and foot size Hair color Skin color Eye color • Many genes on different chromosomes give unlimited phenotype possibilities • A red shorthorn bull may 4. ______________ • Both alleles are expressed in the heterozygous condition be all red, all white, or a combination of red and white hair in the heterozygous (roan cattle) 5. ______________ • This inheritance can also show a hierarchy of dominance from just 4 alleles Two answers needed: 6. ____and______ • Blood groups in Humans have three alleles, two are dominant and one is recessive. • Both dominant alleles show as individual phenotypes when combined in heterozygotes 7. ______________ • A person’s gender is determined by just one set of chromosomes. If the y chromosome is present, the offspring will be a male. 8. ______________ • This inheritance pattern event occurs in females of all mammals as they have XX while males have Xy. This is also called X-inactivation. Example: Calico cats can only be female 9. ______________ • This inheritance pattern results when one allele hides the effect of another allele. • Dominant E allele will determine if the coat will have any dark pigment • Dominant B allele determines how dark the pigment will be 10. ______________ • This inheritance pattern is more likely to be present in males than in females. Traits are found on the X chromosome which men only have Xy 11. _____&_____ • This inheritance is more likely to be present in males than females, and females could be a “carrier” without showing any symptoms. • Can males be a carrier of a recessive hemophilia allele? _______ 12. What has to happen for a girl to be colorblind? • _________________ 13. What can we learn from a Karyotype? Give two answers:_______ and _______ Answers: • • • • • • 1. codominance 2. incomplete dominance 3. polygenic inheritance 4. codominance 5. multiple alleles 6. multiple alleles and codominance • 7. sex determination • 8. dosage compensation • 9. epistasis • 10. x-linked • 11. x-linked, no • 12. A girl who is colorblind must get a colorblind gene from her mom and her dad must be colorblind (XbXb) • 13. number of chromosomes, sex of offspring, if any nondisjunctions have occured