* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
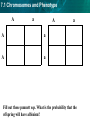
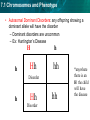
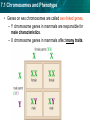
7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype KEY CONCEPT The chromosomes on which genes are located can affect the expression of traits. 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Sexually reproducing organisms have two of each chromosome. •One from mother and one from father •Have the same genes, but may have different alleles • About 99.9% of all human DNA is identical 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Autosomal genetic disorders: disorders that have no relation to the sex of an individual – Autosomal recessive disorder: Any offspring with two recessive genes (cc) will have the disease/disorder – A carrier is heterozygous (Cc) for a recessive disorder C C c CC c Cc *carrier Cc cc *carrier Disorder Ex: Cystic Fibrosis 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype – Albinism is a autosomal recessive disorder characterized by a lack of pigment I skin, hair and eyes. 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype A a A A a A a a Fill out these punnett sqs. What is the probability that the offspring will have albinism? 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype A a A AA Aa A AA Aa • O% will have albinism • 50% carriers A a a Aa aa a Aa aa • 50% will have albinism • 50% carriers Both Mom and Dad have to either have the disorder or be carriers for offspring to be affected with an autosomal recessive disorder! 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Autosomal Dominant Disorders: any offspring showing a dominant allele will have the disorder – Dominant disorders are uncommon – Ex: Huntington’s Disease H h Hh h hh Disorder h Hh Disorder hh *anywhere there is an H the child will have the disease 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Genes on sex chromosomes are called sex-linked genes. – Y chromosome genes in mammals are responsible for male characteristics. – X chromosome genes in mammals affect many traits. 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Male mammals have an XY genotype. – All of a male’s sexlinked genes are expressed because Males have no second copies of sexlinked genes. » One copy X, one copy Y 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype • Female mammals have an XX genotype. – Expression of sex-linked genes is similar to autosomal genes in females. – X chromosome inactivation randomly “turns off” one X chromosome – ensures that females, like males, have one functional copy of the X chromosome in each body cell X 7.1 Chromosomes and Phenotype Males only have one X chromosome so one color will be present (recessive OR dominant) Female cats have two X chromosomes. Each patch of fur can be different depending on which X chromosome “turns off”