* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA - TeacherWeb
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
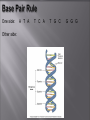
DNA stands for: D: Deoxyribose N: Nucleic A: Acid DNA is too small to see, but under a microscope it looks like a twisted up ladder! Every living thing has DNA. That means that you have something in common with a zebra, a tree, a mushroom and a beetle!!!! 1800’s Scientists know that the nuclei of cells contain large molecules called nucleic acids. 1950 chemist learn DNA is made of but not how it is arranged 1952 Rosalind Franklin that DNA is two chains of molecules in a spiral form • established by James Watson and Francis Crick • Shape of a double helix 4 nitrogen bases (rungs of the DNA ladder) Adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine Which are abbreviated A, G, C, and T The amount of C = amount of G The amount of A= amount of T One side: Other side: A T A T C A T G C G G G The combination of A,T,G,C determines what traits you might have, for ex. C A T C A T = purple hair T A C T A C = yellow hair DNA unzips and replicates new base pairs to match the existing ones on each strand Sections of DNA on a Chromosome Contain instructions for making specific protein Contain the information needed to make specific proteins Each chromosome contains hundreds of genes Ribonucleic Acid Like DNA but only one side of the ladder 3 kinds of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (mRNA) 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) 2. RNA carries the codes for making proteins from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm a. Messenger RNA carries the code that directs the order in which the amino acids bond b. Ribosomal RNA makes up Ribosomes, where proteins are built c. Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the protein. 3. Cells use only the genes that directs the making of proteins needed by that cell. RNA carries the "message" to the ribosomes, where proteins are made 1. 2. Can be caused by outside factors like Xrays, sunlight, and some chemicals have been know to cause mutations. A change in a gene or chromosome can change the traits of an organism. A. B. C. D. E. F. DNA A = adenine T = Thymine Phosphate Sugar (deoxyribose) G = Guanine C = Cytosine