* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Graphs for Macroeconomics Production Possibilities Curve G o
Survey
Document related concepts
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Real bills doctrine wikipedia , lookup
Virtual economy wikipedia , lookup
Balance of payments wikipedia , lookup
Currency war wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Foreign-exchange reserves wikipedia , lookup
Austrian business cycle theory wikipedia , lookup
Phillips curve wikipedia , lookup
Early 1980s recession wikipedia , lookup
Modern Monetary Theory wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Fear of floating wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
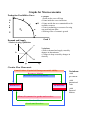
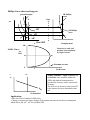
Graphs for Macroeconomics Production Possibilities Curve A B G o o d W C D F X Concepts: • Points on the curve-efficient • Points inside the curve-inefficient • Points outside the curve-unattainable with available resources • Gains in technology or resources favoring one good both not other. • Showing effect of economic growth E Good Y Demand and Supply √ Market clearing equilibrium P S Variations: • Shifts in demand and supply caused by changes in determinants • Changes in slope caused by changes in elasticity Pe D Qe Q Circular Flow Model-basic Land, Labor, Capital & Entrepreneruial Ability Resource Market Resource Money Payments Businesses Variations: • Add government Households • Add International Trade • Add Financial Markets Money Payments for goods and services Product Market Goods and Services Four phases of the business cycle Real GDP Long-term Growth Rate THE BUSINESS CYCLE Peak—prosperity Recovery—Expansion Recession— Contraction Trough—Depression Periods of Time Equilibrium using Aggregate Demand and Supply … occurs at the intersection of the Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply curve setting the equilibrium price level and output. Qf is the output at full employment. Classical-Keynesian Model Extended AD/AS Model AS P r i c e Equilibriu P L e v e l A Q Qf Real GDP P r i c e ASlr ASsr L e v e l AD Qf Real GDP Applications: • Macro instability—inflationary gap, recessionary gap • Fiscal and monetary policy actions and their effects on AD, ASsr, ASlr PL and Real GDP Phillips Curve-short and long run potential output LR Phillips curve A PL d b AD2 a AD1 c e AD3 Rate of I n f l a t I o n d b SR Phillips curve a c e n Real GDP Unemployment 100 Incentive to work and produce is not displaced by high tax rates. Laffer Curve Tax Rate m m Maximum revenue 0 i % l Tax Revenue Sm Money Market…supply of money is a Dm vertical line since monetary authorities (FED) and financial institutions have provided the economy with a certain stock of money. The Price axis is the rate of interest and $$ is the amount of money demanded at that rate. $$ demanded Application: • Show the effect of changes in FED policy • Changes in interest rate causes changes in investment and interest rate-driven consumption, which affects AD, ASsr, ASlr PL and Real GDP. S Loanable Funds Money Market… The real Interest rate is i% i% D Q determined here . Fewer investment projects will be undertaken when the interest rate rises. More investment projects will be undertaken when the interest rate falls. Interest rate includes Expected inflation. Q of loanable funds Applications: • As new demand and supply factors impact this market, changes in interest rate causes changes in investment and interest rate-driven consumption, which affects AD, ASsr, ASlr PL and Real GDP. • When government financing deficit spending, the impact of borrowing increases the demand curve and raises interest rates. • When savings rates rise and fall, the supply curve moves right and left, changing interest rates. Freely floating (flexible) exchange rates The demand for any currency is down $ Price of sloping because as the currency becomes Foreign less expensive to obtain, people will be able Currency to buy more of that nation’s Goods & Services and therefore need more of that currency. The supply is upsloping because as its price rises, holders obtain more of their currencies more cheaply and will want to buy more important goods and therefore give up more of their currency to obtain th i S The intersection will be the exchange rate. D Quantity of Foreign Currency Applications: • Appreciation and depreciation of currency due to changes in price level, interest rates, prosperity abroad, tastes and speculation