* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Summing up the solar system
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Kepler (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Exoplanetology wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
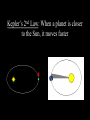
SUMMING UP THE SOLAR SYSTEM Formation of the Solar System Nebular Hypothesis– 12 billion years ago a giant nebula (cloud of gas & dust) rotated quickly, shrank, & compressed creating the sun and a planetary disc. As time passed, the disc condensed into small planets. 4.6 billion years ago, most planets had formed, including Earth! Models for Our S.S. Aristotle & Ptolemy 90-168 A.D. geocentric model of our S.S. Earth is at the center Copernicus 1473-1543 A.D. heliocentric model for our S.S. Sun is at the center Kepler Explained the motions of planets with 3 laws– observed planet orbits from different places on Earth Kepler’s 1st Law Elliptical Orbits not Circular, with the Sun at one foci Ellipse Geometry You do not have to copy this slide Major Axis Foci Minor Axis Eccentricity=How oval is it? Kepler’s 2nd Law Perihelion- planet’s closest distance to Sun in orbit Moves faster than @ aphelion Aphelion- planet’s farthest distance from Sun 2nd Law- “Equal Area Law” b/c the planet has to move faster closer to the sun to get an area equal to that of an area furthest from the sun Click below for an Animation! http://www.physicsclassroom.co m/mmedia/circmot/ksl.cfm Kepler’s 2nd Law: When a planet is closer to the Sun, it moves faster Kepler’s 3rd Law The more distant a planet’s orbit is from the Sun, the slower it moves Compares planets to one another Period- time for one complete orbit around sun Let’s see all three in action Measuring Distances in our S.S. Astronomical Unit (AU) the distance from Earth to the Sun (150 million kilometers OR 93 million miles) Things within our solar system are measure in A.U.’s Other areas within our S.S. 1. The Kuiper Belt: [30-55 AUs] 1000s of objects s.a. dwarf planets and balls of ice/dust/gas (comets or “dirty snowballs”)some get hurled towards the sun comet’s tail always points AWAY from the sun b/c of the solar wind 2. Oort Cloud: [5,000-100,000 AUs] way past the Kuiper belt & Pluto; millions of comets that do not orbit the sun S.S. FACTS 1. Inner planets- “terrestrial” planets 2. Outer planets- “gas giants” or “Jovian planets” 3. Saturn would float in a bowl of water (density is <1.0 g/cm³) 4. All outer planets have rings 5. Venus revolves around the sun quicker than it rotates on its axis (Its day is longer than its year!) 6. Venus is our “sister planet” b/c of its size and density 7. Venus is also known as the “morning star” b/c we can see it in the western sky in the morning S.S. FACTS 8. Venus is the hottest planet b/c of a runaway 9. 10. 11. 12. Greenhouse Effect (too much gas!) Uranus rotates on its side (spins like a bowling ball) Neptune used to have a dark spot, like Jupiter, which was also thought to be a storm Uranus & Neptune are about the same size Jupiter is the largest planet Size of planets in order from largest to smallest 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Earth Venus Mars Mercury Pluto (not a planet) Why was pluto downgraded to a ‘dwarf planet’? 1. Too small ~1 mile across 2. Doesn’t fit the categories of “terrestrial” or “gas” planet- predominantly ice & resides in Kuiper belt (like a comet) 3. Not always the 9th planet– its orbit is so eccentric that it crosses Neptune’s orbital path every 228 years & spends ~20 years being closer to the Sun than Neptune