* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECE 204: Introduction to Electrical Engineering Mathematical Skills
Invention of the integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Digital electronics wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
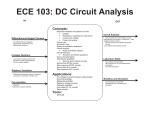
ECE 204: Introduction to Electrical Engineering IN OUT Circuit basics Concepts: Mathematical Skills - Can apply rules and hand-calculate with complex numbers in rectangular, polar, and trigonometric forms - Can solve n x n system of equations - Can represent answer with significant figures DC Circuit Analysis Knows basics of DC circuit analysis: - Current, charge, power, energy - Ohm’s Law, KCL, KVL - Can calculate equivalent resistance N d l d h l i - Current, charge, power and energy - Absorbing and supplying power - KCL, KVL, Voltage and current divider - DC Circuit solving techniques - Req, Leq, Ceq - Independent and dependent sources - First order circuits - Phasor representation of current and voltage - Equivalence between time and frequency domain - Sinusoidal steady-state analysis - Complex power, Instantaneous and average power, apparent power, pf, pf correction - Effective (RMS) values - Balanced three-phase circuits - Magnetic flux and transformers - Ideal and autotransformers - Operational amplifiers - Diodes - Transistors Pre-requisites: - MATH161 and PH142 As of 3/11/13 - Boolean algebra and logic circuits - Truth table - Binary number system - Ones and twos complement - Addition, subtraction and multiplication of binary numbers - Knows basic circuit laws and properties - Understands difference and application of different circuit elements: R, L, C, OpAmp, Transformers, Diodes, Transistors - Knows properties of independent and dependent sources DC and AC Circuit Analysis - Can use mesh and node analysis to analyze circuits with independent sources - Can apply superposition, source transformation, Thevenin and Norton theorems - Knows how to accomplish max power transfer - Can calculate instantaneous and average power - Understands the difference between maximum and RMS value and can apply correct formulas - Understands principles of power factor correction - Can use PQS triangle 1st and 2nd Order Circuits - Can calculate steady state - Can calculate response of a first order circuit - Knows types of responses of a second order circuit Three Phase Circuits - Knows configuration of three-phase circuits - Can tell if a system is balanced or unbalanced OpAmps, Diodes, Transistors, Transformers - Can solve simple circuits with the above elements Boolean, Logic, Binary - Can write expressions for simple logic circuits - Can make a truth table for given expression - Decade to binary, and vice versa - Knows basic operations with binary numbers