* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 20, Section 3 - Sts. Peter And Paul Elementary School
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
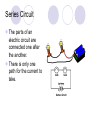
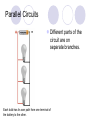
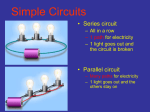
Chapter 20, Section 3 Series and Parallel Circuits Tuesday, January 19, 2010 Pages 662 -- 665 Objectives Describe and construct a series circuit Describe and construct a parallel circuit Vocabulary Words Series circuit Parallel circuit Series Circuit The parts of an electric circuit are connected one after the another. There is only one path for the current to take. Series Circuits Advantages and Disadvantages Advantages Simple to design and build Disadvantages If one part of the series is not working, the entire series won’t work. Bulbs in the series will get dimmer as more bulbs are added (resistance goes up, current goes down). Parallel Circuits Different parts of the circuit are on separate branches. Each bulb has its own path from one terminal of the battery to the other. Parallel Circuit Understanding Parallel Circuit If one bulb burns out in a parallel circuit, the current can still move through the other branches. Switches can be replaced along the branch without affecting the others. Additional branches will decrease resistance. Electric current has more paths to follow so the total resistance is decreased. Household Circuits Circuits in your home are parallel circuits. Lines that carry electricity have very low resistance. Voltage in homes is 120 volts. Switches are located in places where one branch of the circuit is controlled at a time. Homework Workbook 20.3 (due 1/21) Worksheet 20.3 (due 1/21) Vocabulary quiz (1/21)