* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - MIT Section X
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
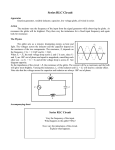
ELE 1001: Basic Electrical Technology Lecture 5 Inductor Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Overview of topics What is an Inductor? Transient behavior of an Inductive circuit Inductor as an energy storage element. Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Inductors Inductor is a passive electric device that stores energy in its magnetic field when a current flows through it A coil of wire wound on a core Air core Inductor, iron core inductor Circuit representation is Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Inductive Circuit Inductance (L) : Property which opposes the rate of change of current. The voltage induced in the inductor is proportional to the rate of change of current flowing through it eL = L (di/dt) i v + Unit is Henry (H). L L This proportionality constant is the self inductance or inductance (L) Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Equivalent Inductance In series 𝑳𝒆𝒒 = 𝑳𝟏 + 𝑳𝟐 + … … + 𝑳𝒏 In Parallel 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 𝟏 = + + …….+ 𝑳𝒆𝒒 𝑳𝟏 𝑳𝟐 𝑳𝒏 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Growth of current in an Inductive Circuit Applying KVL, 𝑽 − 𝒅𝒊 𝑳 𝒅𝒕 −𝑹𝒊=𝟎 Initial Conditions, 𝑨𝒕 𝒕 = 𝟎 𝒔𝒆𝒄, 𝒊 = 𝟎 𝑨 Final current & voltage equation, 𝒊= 𝑽 𝑹 𝑹 𝟏 − − 𝒕 𝒆 𝑳 𝑹 𝒗𝑳 = − 𝑳 𝒕 𝑽𝒆 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Growth of current in an Inductive Circuit Time Constant, = L/R Time taken by the current through the inductor to reach its final steady state value, had the initial rate of rise been maintained constant Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Decay of current in an Inductive Circuit Initial current is through inductor is I0 = V/R At t =0, switch is moved from position a to b t0 Applying KVL, 𝑳 𝒅𝒊 𝒅𝒕 +𝑹𝒊=𝟎 Using initial conditions and solving, 𝒊 = 𝑰𝟎 ( 𝒆 𝒗𝑳 = −𝑽 ( − 𝑹 𝑳 𝒕 ) R a V b 𝑹 − 𝑳 𝒕 𝒆 ) Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering i v L L Decay of current in an Inductive Circuit Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Energy Stored in an Inductor Instantenous power , 𝒅𝒊 𝒑 = 𝒗𝑳 . 𝒊 = 𝑳 𝒊 𝒅𝒕 Energy absorbed in ‘dt’ time is 𝒅𝒘 = 𝑳 𝒊 𝒅𝒊 Energy absorbed by the magnetic field when current is increased from 0 to I amperes, is 𝑰 𝟏 𝟐 𝑾= 𝑳 𝒊 𝒅𝒊 = 𝑳 𝑰 𝟐 𝟎 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Summary Inductor stores energy in its magnetic field. When a series RL circuit is connected to a d.c voltage source, there is an exponential growth of current through the inductor and the current decays exponentially when the voltage source is removed. Time constant of a series RL circuit is 𝐿 𝑅 Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering 𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑑𝑠. Illustration 1 An R-L series circuit is designed for a steady current of 250mA. A current of 120 mA flows in the circuit at an instant 0.1 sec after connecting the supply voltage. Calculate i) time constant of the circuit ii) the time from closing the circuit at which the circuit current has reached 200 mA. Ans: (i) Time constant = 0.1529 s (ii) t= 0.2461 s Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering Illustration 2 A coil of resistance 8Ω and inductance of 0.5H is connected to 110V d.c supply through a switch. The switch is closed at t=0 seconds. Find Rate of change of current at the instant of closing of switch. Final steady value of current. Time constant of the circuit Time taken by the circuit to rise to half of steady state value of current. Ans: (i) 220 A/s ; (ii) 13.75 A (iii) 0.0625 seconds (iv) 0.04332 seconds Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering