* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1E6_Tutorial 8
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
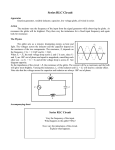
Tutorial No. 8 Problem 1 A circuit having a resistance of 4 , an inductance of 0.5 H and a variable capacitor in series, is connected across a 100 V, 50 Hz supply. Calculate (i) the capacitance to give resonance; (ii) the voltages across the inductance and the capacitance, and (iii) the Q factor of the circuit. Problem 2 Explain the meaning of the term resonance as applied to a series a.c. circuit. Draw the phasor diagram to illustrate this condition A series circuit consists of 0.5 F capacitor, a coil of inductance 0.32 H and a resistance of 40 , and a 20 non-inductive resistor. Calculate the value of the resonant frequency of the circuit. When the circuit is connected to a 30 V a.c. supply at this resonant frequency, determine: (a) the potential difference across each of the three components; (b) the current flowing in the circuit. Problem 3. A constant voltage at a frequency of 1 MHz is maintained across a circuit consisting of an inductor in series with a variable capacitor. When the capacitor is reduced from 300 pF to 284 pF, the current is 0.707 of its maximum value. Find (i) the inductance and the resistance of the inductor, and (ii) the Q factor of the inductor at 1 MHz. Sketch the phasor diagram for each condition Problem 4 Express in rectangular and polar notations, the impedance of each of the following circuits at a frequency of 50 Hz (i) a resistance of 20 in series with an inductance of 0.1 H (ii) a resistance of 50 in series with a capacitance of 40 F, and (iii) the circuits of (i) and (ii) in series. If the terminal voltage is 230 V, 50 Hz, calculate the value of the current in each case and the phase of each current relative to the applied voltage.