* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Populations – Chapter 5
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
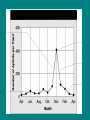
Populations – Chapter 5 Population - A group of organisms that belong to the same species and living within a certain area Vocabulary Terms • Population Density – Number of individuals per unit of area • Population Growth – Increase in the size of the group • Biotic Potential – Highest rate of production possible under ideal conditions ZPG • When a population stays the same it is said that there is zero population growth. • What factors go into determining a growth rate? Determining a Growth Rate 1. Movement out of the area - Emigration Movement into the area – Immigration 2. Number of organisms born – Birth Rate Number of organisms that die – Death Rate For ZPG to occur: • Birthrate + Immigration = Death Rate and Emigration Populations are Changing!! Exponential and Logistic Growth Patterns Trend #1: Exponential Growth • J-Shaped Curve • Ideal environmental conditions • There are no limiting factors holding this population back!! Ex) lots of food and water and space • Population reproduce at a constant rate Trend #2: Logistic Growth • S-Shaped Curve • Logical Growth • Limits on population size based on resources, Limiting Factors, are present An area can only maintain so much and remain stable. • Found only in logistic growth. • Means the number of organisms an ecosystem can maintain over time Carrying Capacity What happens if the population goes over carrying capacity? • The population crashes Graphing Population Trends • Now: Create a graph of the chipmunk population from 1940 to 1995. • Remember to label the x and y axis. • Time always goes on the _______!! • Give it a title! Realistic Growth • In the real world there are limiting factors that eventually come into play as a population gets larger. • The are called limiting factors because they limit the growth rate of a population. • This limit causes the population growth to level off, meaning that the population will reach carrying capacity. Carrying Capacity Factors which cause carrying capacity • Density Dependent: Do not affect all populations the same. Ex) Food, Space, Mates, Disease, Predation • Density Independent: Affect all populations the same despite population size. Ex) Natural Disaster (Flood, Drought, Fire), Pesticides or Poisons, Destruction of Habitat Rabbit Island • Scenario 1: Small Island of 5 Rabbits Climate Food supply Predation • Scenario 2: Small Island of 500 Rabbits Climate – Food Supply – Predation - Summary of Scenario • Which ones changed based on the population size? Food Supply and Predation (These are Density Dependent) • Which ones stayed the same? Climate (This is density independent) Summary Questions • How do you explain the exponential growth pattern in the beginning…what factors affected this growth? • How do you explain the then drastic decline?