* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Relational algebra wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
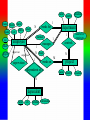
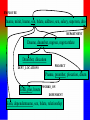
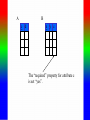
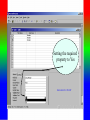
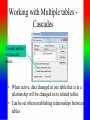
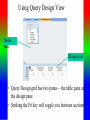
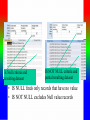
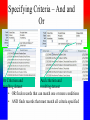
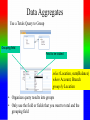
Review: Application of Database Systems ER-diagram Tables and their relationships Application of Database Systems Queries Reports •ER-diagram Entity types Strong entity type Weak entity type Relationships Cardinality constraints Participation constraints Attributes atomic attributes composite attributes single-valued, multi-valued attributes derived attributes key, partial key, surrogate key, non-key attribute name number fname name ssn minit sex 1 lname address salary startdate employee 1 1 1 N hours supervisee N M 1 works on supervision dependents of N dependent sex number of employees controls manages supervisor name department works for N bdate degree location birthdate relationship project name number location Mapping from ER-diagrams onto relational schemas 1. Create a relation for each strong entity type 2. Create a relation for each weak entity type 3. For each binary 1:1 relationship choose an entity and include the other’s PK in it as an FK 4. For each binary 1:n relationship, choose the n-side entity and include an FK with respect to the other entity. 5. For each binary M:N relationship, create a relation for the relationship 6. For each multi-valued attribute create a new relation 7. For each n-ary relationship, create a relation for the relationship EMPLOYEE fname, minit, lname, ssn, bdate, address, sex, salary, superssn, dno DEPARTMENT Dname, dnumber, mgrssn, mgrstartdate Dnumber, dlocation DEPT _LOCATIONS PROJECT Pname, pnumber, plocation, dnum Essn, pno, hours WORKS_ON DEPENDENT Essn, dependentname, sex, bdate, relationship About participation constraints If a relationship is mandatory for an entity set, then if the entity set is on the “many” side of the relationship, then a specification is required to ensure a foreign key has a value, and that it cannot be null •setting the ‘required’ property for the FK in MS Access, or •NOT NULL constraint in the DDL. d A y x 1 N c B A B c d x y c The “required” property for attribute c is set “yes”. Setting the required property to Yes If the entity set is on the “one” side of a relationship, then a check constraint or database trigger can be specified to ensure compliance. d A y x 1 N c B A B c d x y c A program should be produced to check that any value appearing in c-column in table A must appear at least once in c-column in table B. Creating a Table in Design View If you want to create the basic table structure yourself and define all the field names and data types, you can create the table in Design view. Data Types of Fields • Attachment Files, such as digital photos. Multiple files can be attached per record. This data type is not available in earlier versions of Access. • AutoNumber Numbers that are automatically generated for each record. • Currency Monetary values. • Date/Time Dates and times. • Hyperlink Hyperlinks, such as e-mail addresses. • Memo Long blocks of text and text that use text formatting. A typical use of a Memo field would be a detailed product description. • Number Numeric values, such as distances. Note that there is a separate data type for currency. • OLE Object OLE objects (OLE object: An object supporting the OLE protocol for object linking and embedding. • Text Short, alphanumeric values, such as a last name or a street address. • Yes/No Boolean values. Caption property Field Size property • Field Properties can be used to specify characteristics for individual fields • Located in the lower pane of Table Design View Create Tables – Consider a Foreign Key Customer ID - Primary Key in Customer Table Customer ID –will only appear in one record there must only be one unique id per customer Customer ID - Regular Field in Orders Table Customer ID may appear many times – one customer can place many orders • Based on the above example: – Customer Id is the foreign key in the Orders table – This is referred to as a One to Many Relationship • Referential Integrity (i) Consider two relation schemas R1 and R2; ii) The attributes in FK (foreign key) in R1 have the same domain(s) as the primary key attributes PK (primary key) in R2; the attributes FK are said to reference or refer to the relation R2. iii) A value of FK in a tuple (record) t1 of the current state r(R1) either occurs as a value of PK for some tuple t2 in the current state r(R2) or is null. In the former case, we have t1[FK] = t2[PK], and we say that the tuple t1 references or refers to the tuple t2. FK Example: Order(OrderId, …, CustId) Customer(CustId, … ) Working with Multiple Tables – Table Relationships Relationship between two tables • The strength of Access is the fact that it is a relational database – This means you can have multiple tables and create relationships between each table – This helps eliminate redundant data Working with Multiple Tables – Referential Integrity Enforce Referential Integrity • Assures that the references to relationships between data is accurate • Established when creating the relationship between two tables Working with Multiple tables Cascades Cascade update and cascade delete • When active, data changed in one table that is in a relationship will be changed in its related tables • Can be set when establishing relationships between tables Creating a Table with a Query A make table query retrieves data from one or more tables, and then loads the result set into a new table. That new table can reside in the database that you have open, or you can create it in another database. Queries different kinds of queries: - select queries - action queries Make-Table query Delete query Append-Table query Update query - Crosstab query - total queries Group by Aggregate functions: count, sum, maximum, minimum, average - one-to-one relationship, one-to-many relationship Using Query Design View Tables pane Design pane • Query Design grid has two panes – the table pane and the design pane • Striking the F6 key will toggle you between sections Select Query • Searches associated tables and returns a dataset that matches the query parameters Specifying Criteria – Currency and Operands Currency amount entered without dollar sign Greater than (>) operand • Specify criteria with currency – Without the dollar sign – With or without the decimal point • Use operands such as: – Less than and greater than – Equal to or not equal to Is Null criteria and resulting dataset IS NOT NULL criteria and partial resulting dataset • IS NULL finds only records that have no value • IS NOT NULL excludes Null value records Specifying Criteria – And and Or Or Criterion and And criterion and resulting dataset resulting dataset • OR finds records that can match one or more conditions • AND finds records that must match all criteria specified Database Analysis Tools SELECT fname FROM customer WHERE lname=“Smith” ORDER BY fname Returns records in the fname field only where the lname field is equal to Smith. Records are sorted in ascending order by first name • Clauses Added to statements to restrict/specify records • WHERE clause Specifies which records to return • ORDER BY clause Specifies sort order Data Aggregates Use a Totals Query to Group Grouping field Field to be totaled select Location, sum(Balance) where Account, Branch group by Location • Organizes query results into groups • Only use the field or fields that you want to total and the grouping field Reports seven sections: - report header page header group header details group footer page footer report footer