* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MCAS Biology Cell review
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
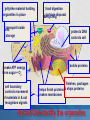
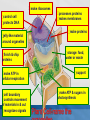
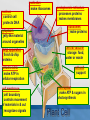
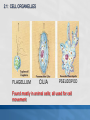
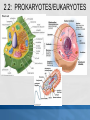
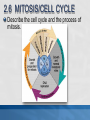
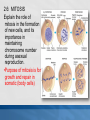
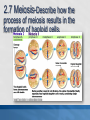
MCAS BIOLOGY REVIEW Cell Biology Ms. Mezzetti Lynn English High School Science Department 2.1: CELL ORGANELLES Relate cell parts/organelles to their functions. ORGANELLE STRUCTURE FUNCTION plasma membrane protects, supports and is semipermeable-allows substances in and out of cell nucleus contains DNA/chromosomes which controls cell’s activities nuclear envelope surrounds nucleus, lets mRNA leave nucleus cytoplasm everything between nucleus and plasma membrane jelly-like material holding organelles in place transport inside cells storage make ATP energy from sugar + O2 cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals food digestion garbage disposal &recycling protects DNA controls cell builds proteins finishes, packages helps finish proteins & ships proteins makes membranes Animal Cell-Identify the organelles cytoplasm jelly-like material holding organelles in place lysosome food digestion garbage disposal &recycling vacuole & vesicles transport inside cells storage mitochondria make ATP energy from sugar + O2 cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals nucleus protects DNA controls cell ribosomes builds proteins Golgi apparatus finishes, packages ER helps finish proteins & ships proteins makes membranes Animal make ribosomes control cell protects DNA processes proteins makes membranes make proteins jelly-like material around organelles finish & ship proteins storage: food, water or waste support make ATP in cellular respiration cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals make ATP & sugars in photosynthesis Plant Cell-name the nucleus control cell protects DNA cytoplasm jelly-like material around organelles Golgi apparatus finish & ship proteins nucleolus make ribosomes endoplasmic reticulum processes proteins makes membranes ribosomes make proteins central vacuole storage: food, water or waste cell wall support mitochondria make ATP in cellular respiration cell membrane cell boundary controls movement of materials in & out recognizes signals chloroplast make ATP & sugars in photosynthesis Plant Cell 2.1: CELL ORGANELLES FLAGELLUM CILIA PSEUDOPOD Found mostly in animal cells; all used for cell movement 2.1 Role of cell membrane Explain the role of cell membranes as a highly selective barrier (diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, and active transport). Role of cell membrane-osmosis Osmosis – diffusion of water 2.2: PROKARYOTES/EUKARYOTES Compare and contrast, at the cellular level, prokaryotes and eukaryotes (general structures and degrees of complexity). PROKARYOTES No nucleus BOTH DNA EUKARYOTES Membrane bound nucleus No membrane Ribosome Membrane bound bound organelles s organelles-ER; golgi bodies; mitochondria; lysosome Bacteria Plasma Animal, plant, membrane protist and fungi cells Simple cells Cytoplasm Complex cells 2.2: PROKARYOTES/EUKARYOTES 2.3 CELLULAR EVIDENCE FOR 6 KINGDOMS Use cellular evidence: cell structure cell number, cell reproduction modes of nutrition to describe the six kingdoms (Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia). 7 LEVELS OF CLASSIFICATION 2.3 SIX KINGDOMS OF LIFE 2.4 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Identify the reactants, products, and basic purposes of photosynthesis and cellular respiration. • Takes place in the chloroplasts of plants • Produces glucose plants convert to starch for storage, cellulose for structure and ATP for energy. 2.4 CELL RESPIRATION Takes place in the mitochondria Process produces ATP Aerobic respiration requires oxygen Anaerobic- no oxygen; fermentation; takes place in cytosol 2.4: Explain the interrelated nature of photosynthesis and cellular respiration in the cells of photosynthetic organisms. • • Plants are autotrophsproduce their own food Animals are heterotrophs-rely on other organisms for their nutrition (food). 2.5 Explain the important role that ATP serves in metabolism. 2.6 MITOSIS/CELL CYCLE Describe the cell cycle and the process of mitosis. 2.6: MITOSIS Explain the role of mitosis in the formation of new cells, and its importance in maintaining chromosome number during asexual reproduction. •Purpose of mitosis is for growth and repair in somatic (body cells) 2.7 Meiosis-Describe how the process of meiosis results in the formation of haploid cells. 2.8 Compare and contrast a virus and a cell in terms of genetic material and reproduction. • • • • Viruses can contain DNA and RNA Viruses can not reproduce on their own They need to invade a host cell to reproduce Bacteriophages invade bacteria; inject their DNA into the host cell