* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 7-Cells Lecture #1 blanks
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Confocal microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
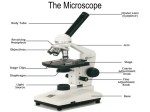
The Discovery of Cells 7.1 I. The Cell Theory A. ____- The basic unit of living organisms B. The ______ was developed by several scientists including Hooke, Schleiden andSchwann. I. The Cell Theory C. 3 Main Ideas 1. All _______ are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of structure and _________ of organisms. 3. All cells come from _________ cells II. Role of the Microscope A. Before microscopes, we didn’t know cells existed 1. People thought illness caused by bacteria were brought by _______ II. Role of the Microscope B. 1st (Simple) Microscope 1. 1600’s 2. Leeuwenhoek 3. Used __ reading lenses and light to view objects II. Role of the Microscope C. Compound Microscope 1. 1600’s 2. _______ observed and named “cells” 3. Uses ______ lenses and light to magnify objects up to 1500 x II. Role of the Microscope D. Microscope practice 1. Observe cork 2. Observe ________ slides II. Role of the Microscope E. Electron Microscope 1. 1930’s 2. Uses an ________ beam instead of light 3. Magnifies up to _______ x II. Role of the Microscope 4. Types of electron microscopes a. ____- Makes a 3-D image of the cell surface b. ____- Magnifies structures inside the cell c. ____- Creates computer images of atoms on a molecule III. Basic Cell Types A. _______- Small, specialized structures in a cell 1. A.K.A. CELL PARTS 2. Surrounded by ________ III. Basic Cell Types B. Prokaryotes (hint: pro means NO) 1. No membrane bound organelles 2. No _______ 3. No more than one cell (Single-celled organisms) 4. No organization III. Basic Cell Types C. _____________ 1. DOES have membranebound organelles 2. DOES have a nucleus 3. Single-celled or multicelled organisms 4. Think of these as being more complex/organized IV. Recap What are the 3 main ideas of the cell theory? What is the difference between a simple, compound and electron microscopes? What is the difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote?