* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
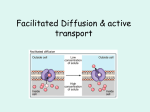
On a notecard write your answer Bellringer: In one or two complete sentences describe what the following quote tells us about the origin of new life. Quote: “Fireflies rise from the morning dew, fish and frogs from a muddy stew, maggot worms from rotting meat and mice shall come from sweat and wheat.” Cell Theory and the Scientists Who Helped Shape It What is Spontaneous Generation? the belief that living things can come from non-living things. Was once thought to be true, but is now known to be false! How was it disproved? the following scientists with their combined experiments proved the theory of spontaneous generation to be false & helped develop the Cell Theory. Scientists and the Cell Theory Who was… Francesco Redi? (1668) scientist whose experiments proved maggots did not come from rotting meat. Who was…Robert Hooke? (1665) used a compound microscope to look at cork (from bark of a tree) & he saw empty boxlike structures that he named “cells”. Who was…Antonie van Leewenhooke? (mid 1600’s) used a simple microscope to look at pond water. was the first to observe microorganisms in pond water. Who was…Matthias Schleiden? (1830’s) studied numerous plant parts under the microscope and declared “ALL PLANTS ARE MADE OF CELLS!” Who was… Theodor Scwhann? (mid 1830’s) Used a microscope to observe numerous animal tissues and declared “ALL ANIMALS ARE MADE OF CELLS!” Who was… Rudolf Virchow? (Mid 1830’s) observed living cells dividing and declared “ALL CELLS COME FROM OTHER LIVING CELLS!” The Cell Theory Major Contributors: Matthias Schleiden Theodor Schwann Rudolph Virchow The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. Living cells come only from other living cells. Characteristics of All Cells A surrounding membrane Cytoplasm – cell contents in thick fluid Organelles – structures for cell function Control center with DNA Cell Types Prokaryotic Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cells • • • • • First cell type on earth Cell type of Bacteria and Archaea No membrane bound nucleus Nucleoid = region of DNA concentration Organelles not bound by membranes Eukaryotic Cells Nucleus bound by membrane Include fungi, protists, plant, and animal cells Possess many organelles Plasma (Cell) Membrane Plasma Membrane Contains cell contents Double layer of phospholipids & proteins Phospholipids Polar Hydrophylic head Hydrophobic tail Interacts with water Movement Across the Plasma Membrane • A few molecules move freely – Water, Carbon dioxide, Ammonia, Oxygen • Carrier proteins transport some molecules – Proteins embedded in lipid bilayer – Fluid mosaic model – describes fluid nature of a lipid bilayer with proteins Membrane Proteins 1. Channels or transporters 3. Glycoproteins – Move molecules in one direction 2. Receptors – Recognize certain chemicals – Identify cell type 4. Enzymes – Catalyze production of substances Molecule Movement & Cells Passive Transport Active Transport Endocytosis (phagocytosis & pinocytosis) Exocytosis Passive Transport No energy required Move due to gradient differences in concentration, pressure, charge Move to equalize gradient High moves toward low Types of Passive Transport 1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis 3. Facilitated diffusion Diffusion Molecules move to equalize concentration Osmosis Special form of diffusion Fluid flows from lower solute concentration Often involves movement of water Into cell Out of cell Solution Differences & Cells solvent + solute = solution Hypotonic Solutes in cell more than outside Outside solvent will flow into cell Isotonic Solutes equal inside & out of cell Hypertonic Solutes greater outside cell Fluid will flow out of cell Facilitated Diffusion Differentially permeable membrane Channels (are specific) help molecule or ions enter or leave the cell Channels usually are transport proteins (aquaporins facilitate the movement of water) No energy is used Process of Facilitated Transport • Protein binds with molecule • Shape of protein changes • Molecule moves across membrane Active Transport • Molecular movement • Requires energy (against gradient) • Example is sodium-potassium pump Endocytosis Movement of large material Particles Organisms Large molecules Movement is into cells Types of endocytosis bulk-phase (nonspecific) receptor-mediated (specific) Process of Endocytosis • Plasma membrane surrounds material • Edges of membrane meet • Membranes fuse to form vesicle Forms of Endocytosis • Phagocytosis – cell eating • Pinocytosis – cell drinking Exocytosis Reverse of endocytosis Cell discharges material Vesicle moves to cell surface Membrane of vesicle fuses Materials expelled