* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 Lesson 3.2
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
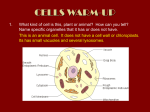
Chapter 3 Lesson 3.2 EUKARYOTIC CELLS Eukaryotic Cells have many parts to help the cell stay alive. They are called ORGANELLES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Cell Wall Cell Membrane Cytoskeleton Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Mitochondria Chloroplasts Golgi Complex Vesicle Lysosomes Vacuoles Add to your list from Science Lab Cytoskeleton – a web of proteins in the cytoplasm – it keeps the cell’s membranes from collapsing, and helps some cells move Only in Plant Cells Not in Animal Cells Cell Wall – Plant cells have cell walls. A cell wall is a rigid structure that gives support to the cell. Chloroplast – Plant cells have chloroplasts – organelles where photosynthesis takes place. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide and water to make sugar and oxygen. Chloroplasts are green because they contain chlorophyll.