* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell-testRvwPPT_Answers to Questions
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
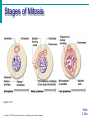
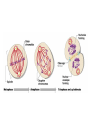
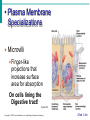
• tRNA = brings Amino Acids to ribosomes (ribosomes helper) • mRNA = Carries genetic code from DNA/inside nucleus to ribosomes • Transcription – Re-writing DNA code into mRNA • Translation – Bldg. the protein (by ribosome reading mRNA) • Hypertonic – greater # solutes outside of cell • Hypotonic – lower # of solutes outside of cell • Passive transport – No energy used to inport/export substances • Diffusion – moving from high-low conc. • osmosis – diffusion of Water(diffusion just special term when its water) • Facilitated diffusion – use of carrier proteins to inport/export….still no energy • Active transport – cell uses energy to inport/export substances. • When used: Big molecules (ex. Proteins) – Trasporting against a concentration gradient. – Other material not able to pass/diffuse (non-lipid soluble) • Exocytosis – cell pckgs material in vesicle for export…moves to plasma (cell membrane)…merges w/membrane then spills outside of cell. • Important for any secretory cells---Pancreas (insulin=modified protein) • Endocytosis – plasma memb. Engulfs material (food, water,etc). • Phagocytosis – “cell eating” • Pinocytosis - “cell drinking” • • • • • Phases of Mitosis PMAT: Prophase: centrioles migrate to opp. Poles Metaphase: Chromosomes align in Middle Anaphase: Chromosomes pulled Apart by spindle fibers • telophase: Cell begins to split..become two; cleavage furrow. Stages of Mitosis Figure 3.14; 1 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Slide 3.36a • Plasma Membrane Specializations Microvilli Finger-like projections that increase surface area for absorption On cells lining the Digestive tract! Figure 3.3 Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Slide 3.8a Hydro___?___ Hydro___?___ Stabilizes/stiffens plasma membrane Cell organelles - Function • Lysosome – vesicles of digestive enzymes • Mitochondria – “powerhouse of the cell”, site of cellular respiration (ATP production) • Golgi Apparatus – “fedEx of Cell”, packages proteins for delivery in/out of cell • Endoplasmic Reticulum – “highway of the cell”, transports proteins throughout cell. – Rough E.R. = has Ribosomes – Smooth E.R. = no ribosomes • Nucleolus – makes ribosomes, inside nucleus • Nucleus – contains DNA, “control center of Cell”…..DNA is genetic code. • Cytoplasm – portion of cell outside of nucleus where cell organelles are located. – Cytosol – gel-like fluid of the cytoplasm • Cytoskeleton – provides structure/support to cell, “I-beams of cell – Microtubules make largest part of cytoskeleton, also microfilaments & intermediate fibers. Ribosomes – Make proteins Cilia – hair-like projections on plasma membrane that move substances across the cell. Cells of Respiratory Tract=perfect ex. Constantly moving inhaled particles (pollen,smoke) upwards away from deep lung. Flagella: whip-like structure that propels the cell, Sperm cell in humans.