* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocytosis - Cloudfront.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
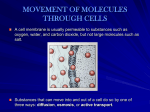
• Diffusion: Movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration • Movement continues until equilibrium is reached • Equilibrium: same amount of molecules on the outside of a cell as the inside Diffusion (contd) • Passive transport: No energy required to move molecules • If more molecules outside the cell… they move inside • If more molecules inside the cell…they move outside • Will O2 move into this cell or out of this cell? Diffusion (contd) Where is the high Oxygen concentration? Where is the high CARBON DIOXIDE concentration? • Passive transport: No energy (ATP) required to move molecules • If more molecules outside the cell… they move inside (and vise versa) Where is the HIGH oxygen concentration? Where is the LOW oxygen concentration? Where is the HIGH oxygen concentration? Where is the LOW oxygen concentration? Cell X gets oxygen through the process of diffusion! The reverse process is true w/ carbon dioxide. Where is the HIGH carbon dioxide concentration? Where is the HIGH carbon dioxide concentration? Osmosis • Defined: Diffusion of water from an area of high to low concentration • High H20 concentration if: less particles dissolved in the water • Low H20 concentration if: more particles dissolved in the water • Dots represent dissolved particles (not water molecules) Group Explanation A cell has been placed into a mystery solution and appears to have shrunken. 1) Which type of solution is the cell placed in? 2) What can you conclude about the water concentration inside the cells compared to outside? 3) What can you conclude about the solute concentration inside the cells compared to outside? 4) Using your explanation of osmosis, explain why the cell appears to have shrunken. A cell has been placed into a mystery solution and appears to have shrunken. 1) Which type of solution is the cell placed in? hypertonic 2) What can you conclude about the water concentration inside the cells compared to outside? If the cell shrunk it lost water. This means the cell had a greater water concentration. 3) What can you conclude about the solute concentration inside the cells compared to outside? The solute concentration inside the cell is low. I know this because the cell has a high water concentration. The fewer solutes, the higher the water concentration. 4) Using your explanation of osmosis, explain why the cell appears to have shrunken. The cell shrunk because it lost water. There was a greater water concentration inside the cell so therefore water diffused out of the cell. Facilitated Diffusion • Defined: Larger molecules enter/exit with the help of protein channels in the plasma membrane • No energy is required (passive) • Q: Why are the molecules exiting this cell and not entering? • A: There are more molecules inside than out Active Transport • Defined: Molecules move from a LOW to a HIGH concentration • ATP energy opens/closes protein channel – ATP = Adenosine Triphosphate • Acts like a pump Contractile vacuole of a Paramecium Water being pumped out of this cell to prevent bursting Endocytosis • Endocytosis: Process in which the plasma membrane takes in substances (2 types) – 1) Phagocytosis: when a cell engulfs a solid particle – 2) Pinocytosis: when a cell engulfs a liquid particle • Unfortunately, viruses can also enter our cells this way Endocytosis & the lysosome Exocytosis • Defined: Process when substances are expelled from the cell • Proteins, nutrients, and waste exit by exocytosis • Vesicle carry & release objects through the plasma membrane Quick Review • Diffusion is the movement of particles from high to low concentrations • Some methods of movement don’t require energy (Passive Transport) • Some methods of movement require energy (Active transport) • Farts smell because of diffusion