* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Growth and Division
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
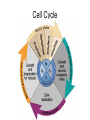
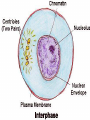
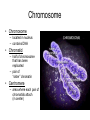
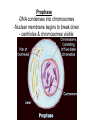
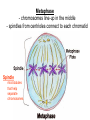
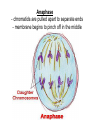
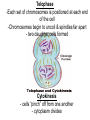
Chapter 10: Mitosis Cell Growth and Division Cell Division • Cell Division – cell divides into two new IDENTICAL “daughter cells” • Mitosis – division of nucleus during eukaryotic cell division • Cytokinesis – division of cytoplasm during eukaryotic cell division Cell Cycle Interphase • Interphase – portion of cell cycle between divisions – ~ 75 – 80% life of cell – 3 phases: • G1: cells grow and develop • S: chromosomes replicate • G2: organelles required for division reproduce Chromosome • Chromosome – located in nucleus – contains DNA • Chromatid – half of chromosome that has been replicated – pair of “sister” chromatin • Centromere – area where each pair of chromatids attach (in center) CHROMOSOME sister chromatid centromere sister chromatid Mitosis • Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase “Please Make Another Test” 1. Prophase – doubling of chromosomes & organelles – centrioles visible • 2. Metaphase – chromosomes line-up in the middle – spindles from centrioles connect to each chromatid (half of chromosome) • 3. Anaphase – chromatids are pulled apart to separate ends – membrane begins to pinch off in the middle • 4. Telophase – – – – Nucleus and nuclear envelope reform Chromosomes decondense and disappear (you can no longer see them) Cytokinesis - complete division of cytoplasm two daughter cells formed Prophase -DNA condenses into chromosomes -Nuclear membrane begins to break down - centrioles & chromosomes visible Metaphase - chromosomes line-up in the middle - spindles from centrioles connect to each chromatid Spindle microtubules that help separate chromosomes Anaphase - chromatids are pulled apart to separate ends - membrane begins to pinch off in the middle Telophase -Each set of chromosomes is positioned at each end of the cell -Chromosomes begin to uncoil & spindles far apart - two daughter cells formed Cytokinesis - cells “pinch” off from one another - cytoplasm divides http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pl uginpop.cgi?it=swf::5 35::535::/sites/dl/free/ 0072437316/120073/ bio14.swf::Mitosis%2 0and%20Cytokinesis Regulating the Cell Cycle • Cyclins – Proteins that stimulate division during growth and repair (Interphase) – Internal regulators • respond to the events inside the cell – External regulators • speed up or slow down the cell cycle Cancer • Cancer = uncontrolled cell growth – do not respond to signals that regulate growth – causes: heredity, chemicals, radiation • Tumors = unregulated cell growth – Benign: cells stay together – Malignant: cells spread and grow elsewhere - invade healthy tissues