* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
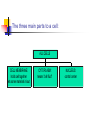
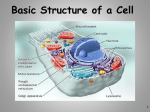
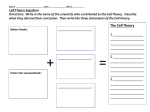
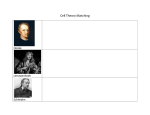
Introduction to Cells! Recall the Cell Theory: All living things are made of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. (Therefore, all living things come from other living things.) Robert Hooke England (1665) Used a very simple microscope Looked at many things (feathers, fish, fly wings, fungi) One day he looked at a slice of cork under his microscope. They reminded him of the little rooms where monks prayed. This is his actual drawing of what he saw. So what is Hooke remembered for? At the same time, a man named Anton van Leeuwenhoek was also looking through a simple microscope. Anton van Leeuwenhoek Holland (1673) He looked at blood from many animals. He also looked at pond water. Called them “animalcules”. How is his discovery different from Hooke’s? So what ARE cells? many shapes many sizes many colors many different functions Cells have many parts, but all cells have these three MAIN parts: cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus The three main parts to a cell: ALL CELLS CELL MEMBRANE: holds cell together lets some materials in/out CYTOPLASM: means "cell fluid" NUCLEUS: control center