* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells into Tissues
Survey
Document related concepts
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Gap junction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
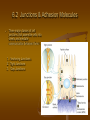
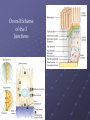
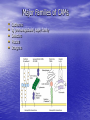
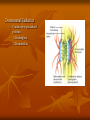
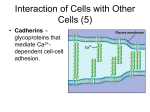
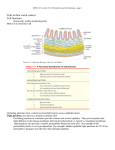
Cells into Tissues By Kevin Huyen 6.1 Cell-Cell and Cell-Matrix Adhesions • Cell-adhesion molecules (CAMS) mediate direct cell-cell adhesions • Cell-surface adhesion receptors mediate cell-matrix (ECM) adhesions. These interactions bind cells into tissues and facilitate communication between cells and their environment 6.2 Junctions & Adhesion Molecules Three major classes of cell junctions that assemble cells into sheets and mediate communication between them. 1. Anchoring Junctions 2. Tight Junctions 3. Gap Junctions Anchoring Junctions Are specialized regions of the cell surface containing CAMs or adhesion receptors that interact with other cells, the ECM, or cytoskeletal fibers. Two Major Types: Mediate cell-cell adhesion Adherens junctions Desmosomes Mediate cell-matrix adhesion Hemidesmosomes Tight Junctions Type of cell-to-cell junction that prevents diffusion of macromolecules and many small molecules and ions in the spaces between cells. Specifically, they limit and regulate the extracellular flow of water and solutes. Gap Junction Permit the rapid diffusion of small, water-soluble molecules between the cytoplasm of adjacent cells. Overall Scheme of the 3 Junctions 6 Major Families of CAMs • • • • • Cadherins Ig (immunoglobulin) super family Selectins Mucins Integrins Cadherin Family Found in Adherens junctions and desmosomes Cadherins are key molecules in cell-cell adhesion and cell signaling. Adheren Junction Desmosomal Cadherins Contain two specialized proteins 1) Dismoglein 2) Dismocollin Selectins Family of CAMs that mediate leukocyte-vascular cell interactions. Extravasation of leukocytes require the successive formation and breakage of cellcell contacts between leukocytes in the blood and endothelial cells lining the vessels Blood Sialyl Lewis-x antigen Sugar binding lectin domain P-selectin Endothelial cell Purpose of Selectins Integrins A large family of alpha beta heterodimeric cell surface proteins that mediate both cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesions Integrins typically exhibit low affinities for their ligands IIb3 integrin platelet *Accelerates a formation of clotting Collagen or factors thrombin Conformational change of IIb3 integrin platelet Fibrinogen Activated platelet Summary Cell to cell contact through cell adhesion molecules or adhesion receptors Summary (continued) 3 types of specific types of adhesions called Junctions are: Anchoring Tight Gap