* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
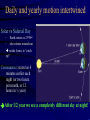
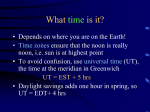
Scaling & Daily Motion Scaling • Often one is interested in how quantities change when an object or a system is enlarged or shortened • Different quantities will change by different factors! • Typical example: how does the circumference, surface, volume of a sphere change when its radius changes? How does it scale? • Properties of objects scale like the perimeter, the area or the volume – Mass scales like the volume (“more of the same stuff”) – A roof will collect rain water proportional to its surface area Daily Rising and Setting • Due to the rotation of the Earth around its axis • Period of rotation: 1 siderial day= 23h56m4.1s • 1 solar day (Noon to Noon) =24h • Stars rotate around the North Star – Polaris What time is it? • Depends on where you are on the Earth! • Time zones ensure that the noon is really noon, i.e. sun is at highest point • To avoid confusion, use universal time (UT), the time at the meridian in Greenwich UT = EST + 5 hrs • Daylight savings adds one hour in spring, so UT = EDT+ 4 hrs The Time Zones Established to insure that sun is at highest point approximately at noon in the middle of the time zone Daily and yearly motion intertwined Solar vs Siderial Day – – Earth rotates in 23h56m also rotates around sun needs 4 min. to “catch up” Consequence: stars rise 4 minutes earlier each night (or two hours per month, or 12 hours in ½ year) After 1/2 year we see a completely different sky at night!