* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Science Hill Visual Art
Survey
Document related concepts
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Early Netherlandish painting wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Art in the Protestant Reformation and Counter-Reformation wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
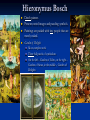
Italian and Northern Renaissance Early Renaissance Basic History Florence is the birthplace of Renaissance. Early Renaissance was an era of extreme stress and conflict The crowning jewel of the Florentine cityscape is the cupola, or dome, of its cathedral. This architectural and engineering wonder was designed by Filippo Brunelleschi. Filippo Brunelleschi Brunelleschi was a goldsmith, sculptor, mathematician, clock builder, and architect (his greatest achievement). He discovered scientific perspective, a way of accurately showing 3-D objects on flat paper. In Florence, 1418, he won a competition to design the mammoth dome over the Cathedral of Florence. He concluded that discipline of thought, clarity of design, the proportion of one part to another, and a constant awareness of regular visual rhythm are essential to fine architecture. Lorenzo Ghiberti sculptor Won the competition for the design and sculpting of the north doors of the baptistery of Florence at 21 years old. The two doors took more than 20 years to complete. The 28 panels illustrate stones from the New Testament as well as other figures. The doors were later called the Gates of Paradise. He used pictorial space and one-point perspective to produce convincing depths on relief sculpture. The doors were true Renaissance art and were cast in bronze, covered with gold. Donatello sculptor Emerged as the greatest sculptor of his time and ever to live. His work was a combination of Classical style and Renaissance expression. His figures seemed capable of movement and the facial expressions provided images of pride and dignity. Many of his figures were either marble or bronze. His figure, David, made of bronze, was first lifesize freestanding nude statue since ancient times. Masaccio painter Revolutionized the art of painting. Painted “Tribute Money” A fresco in the church of Santa Maria del Carmine. A New Testament illustration that depicts three events at one time. Used single source of light and atmospheric perspective to add the sense of depth. Sandro Botticelli painter Responsible for the painting “Birth of Venus”, which is an example of a scene based on traditional mythology. Baptism, like the birth of the Celestial Venus, signifies the rebirth of humanity He was a master of delicate lines. “The Adoration of the Magi” reveals another characteristic of late 15th century paintings; the wise men and others as portraits of Italian contemporaries. High Renaissance Basic History From 1495-1527, powerful and ambitious popes created a new force in Italy, a papal state, with Rome as its capital. Rome took lead from Florence and became the art capital of Europe. Leonardo da Vinci He was an artist ahead of his time in painting, sculpture, architecture and many other professions. The Mona Lisa is his most famous painting. Used sfumato and created a hazy feeling and aerial perspective. He carried this painting with him until he died. Used chiaroscuro (extreme contrast of dark and light values) in his paintings. Michelangelo Buonarroti His artistic genius influenced the late Renaissance and beyond. Pieta His earliest masterpiece, a sculpture made of marble. Was not concerned with exact proportions but rather the overall appearance and visual effect. Signed this work on a band across Mary’s chest. David Muscular perfection and an expression that is angry and defiant. Believed that human beauty is the outward indication of divine spirit. At 21, he is declared the greatest sculptor in Italy. Raphael Sanzio Raphael’s paintings are known as masterpieces of balance and harmony. School of Athens Shows all the masters of Classical Greek thought, science and art are in animated conversations. The setting is dramatic and in harmony with the number and placement of figures. Titian Artistic giant of Venice, comparable to Michelangelo. Believed that color and mood were more important in painting than line and scientific accuracy. After paint was dry, the surface was painted with about forty glazes, In later work no outlines, color blended into color to create form. Brushstrokes created a textured surface quality called painterly. Mannerism Basic History Refers to the period between the end of the High Renaissance and the beginning of the Baroque period. Was originally a derogatory term applied to painters who had a formal, mannered style that imitated various aspects of Raphael’s and Michelangelo’s works. Included in the Mannerist style are features such as crisp and frozen shapes, elongated bodies, distorted forms, and peculiar perspectives. El Greco Born in Crete In his artwork there is a strong sense of movement, form is often dematerialized. Painted many religious works. The Burial of Count Orgaz The artists masterpiece The lower part is 16th century on earth, the upper is eternal and in heaven. Sofonisba Anguissola Was the oldest child of a wealthy family in Cremona Her paintings are charming and informal Her artwork captures the act of everyday life. Tintoretto Most dramatic painter of the 16th century. Tintoretto means “little dyer”, which is his fathers occupation. Most his paintings are religious. Would make small models to see shadows. Worked for small salary, most paintings done for charity houses. Giovanni Bologna Most original sculptor between Michelangelo and Bernini. Most artwork up to this time has been viewed from front, back and profile, but his work had no front or back, the viewer must move constantly to see the complete work. Andrea Palladio The only northern Italian architect that ranks with Bramante and Michelangelo. Several palaces, theatres, and town halls were designed and built by him. Wrote and illustrated a book on his thoughts and ideals that was used up until the 18th century. The Low Countries Basic History The Gothic style of architecture dominated northern Europe into the early 16th century. The painters of low countries (Belgium and Holland) were first to master oil paint. Painters aimed at clear, hard edged detail and was one of radiant decorative color rather than sculptural form. Artists in low countries accomplished religious subjects in scenes of everyday life by using symbolism. Jan van Eyck His understanding of light was far greater than that of his Italian Contemporaries. He excelled at portraying direct and diffused light, shadows falling on a variety of surfaces, and light’s effect on the illusion of distance. Ghent Alterpiece Was begun by Hubert van Eyck in 1425 and finished by his brother Jan 7 years later. Landscapes, animals, trees, people, fabrics, light and air are handled with detail. Jan van Eyck The Annunciation The angel Gabriel announces the Birth of Christ to Mary. The event takes place in a 15th century Gothic church. Arnolfini Wedding A work of marvelous reality and unity. Detail and realistic light share importance in this painting. Signed his name on the wall above the mirror with words meaning “Jan van Eyck was here in 1434” Hieronymus Bosch Dutch painter. Presents weird images and puzzling symbols. Paintings are packed with tiny people that are mostly naked. Garden of Delights Most complex work Three full panels of symbolism On the left – Garden of Eden, on the right – Garden of Satan, in the middle – Garden of Delights Pieter Bruegel He was the most highly acclaimed low country master of the 16th century. He was said to be the only artist to capture the cold and crispness of winter. The Return of the Hunters Loved to paint peasants in their daily activities. The depth is felt more strongly because of the birds flying in the intervening space. Humans and nature are bound together as a working unit. Germany Basic History In the early 1500’s, Germany becomes the leader in art in Northern Europe. German artists absorb the influence of the Italian High Renaissance and blend it with northern technique and style. Albrecht Durer Leader of the German High Renaissance. Was the first artist outside of Italy to become internationally acclaimed. Also first northern artist to very consciously document himself in a series of self-portraits. Durer and Printmaking First artist to emerge from medieval anonymity with a distinct personality. Was the 3rd of 18 children and after he had completed elementary school, he was taken on as apprentice to his goldsmith father. Was very talented in both woodcut and copper engraving. One of the first artists to turn to woodcut as a major medium. The market for his works was huge and he became a wealthy artist. Matthias Grunewald Was the last and most powerful of the expressive Gothic artists. He painted only a limited number of works but his single greatest masterpiece is the Isenheim Alterpiece. Hans Holbein One of the finest portrait painters of all times. Born in Germany but moved to Basel, Switzerland when he was about 13 and stayed there for 11 years. One of his greatest achievements is his double portrait The French Ambassadors England, France, and Spain Basic History England France The Renaissance brought the English language and literature in works by Shakespeare and others. The “International Style” originated in Burgundy and continued in painting. Two important artists were Jean Fouquet and Jean Clovet. Francis I and the French aristocracy built a group of opulent chateaux in the Loire River Valley. Spain Very wealthy at this time. El Escorial Constructed for Phillip II of Hapsburg. Architect was Juan de Herrera. A combination of a palace and court with a church. Made of granite. Expressed the unified Catholic spirit. Eleven Spanish kings lie beneath the alter. French Painting Jean Fouquet Most important French artist of the 15th century. Painted portraits and religious scenes and worked on manuscript illuminations Influenced by Italian art His painting Etienne Chevalier and St. Stephen reflects the Flemish influence. French Architecture The Chateau of Chambord Built in 1519 Has a large central block that contains numerous apartments. There’s a rounded tower on each corner. Wings on each side contain simple hallways that terminate in huge rounded fortress-like structures with conical roofs. French Architecture The Square Court of the Louvre First building of the French Renaissance Goujon furnished the structure with sculptures and fine reliefs.