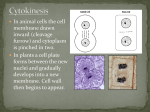
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Visua of the Human Body
Survey
Document related concepts
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
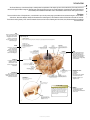
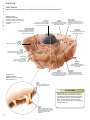
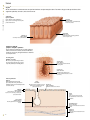
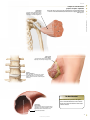
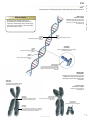
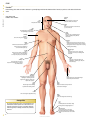
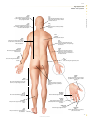
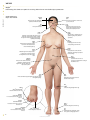
frontal muscle M músculo frontal Large, unpaired muscle connecting the upper part of the orbit and the epicranial aponeurosis; it allows the skin of the forehead to crease and the eyebrows to lift. definitions visuAl of the Human Body English S PA NISH orbicular muscle of mouth M F músculo orbicular de la boca Unpaired muscle having two bundles connecting the corners of the lips, allowing the mouth to open and close especially. greater zygomatic muscle M músculo cigomático mayor Paired muscle connecting the zygomatic bone to the angle of the mouth; it assists in smiling. QA INTERNATIONAL Extrait de la publication Extrait de la publication definitions visuAl Human Body of the English S pa n i s h Extrait de la publication The Visual Dictionary of the Human Body was created and produced by Editor Editorial Director Caroline Fortin QA International 329, rue de la Commune Ouest, 3e étage Montréal (Québec) H2Y 2E1 Canada T: 514.499.3000 F: 514.499.3010 Martine Podesto Editor-in-Chief Anne Rouleau Graphic Designers Mélanie Giguère-Gilbert Josée Noiseux www.qa-international.com Layout © QA International, 2009. All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval sytem, without permission in writing by QA International. ISBN 978-2-7644-0900-8 Printed and bound in China. 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 14 13 12 11 10 9 Émilie Corriveau Pascal Goyette Danielle Quinty Illustrators Art Director: Sylvain Bélanger Danielle Bader Manuela Bertoni Jocelyn Gardner Mélanie Giguère-Gilbert Alain Lemire Raymond Martin Émilie McMahon Anouk Noël Programmer-analyst Éric Gagnon Project Managers Nathalie Fréchette Véronique Loranger Prepress Julien Brisebois François Hénault Karine Lévesque Patrick Mercure Proofreading Myriam Caron Belzile Claude Frappier Veronica Schami Scientific Advisor Dr. Éric Philippe, Ph. D. This book is part of a larger encyclopedic project on health in general. About 300 specialists from America and Europe participated in the scientific validation of texts and illustrations produced for this project: Sylvie Louise Avon, D.M.D., M. Sc., CS (ODQ), FRCD(C), Faculty of Dentistry, Université Laval; Abdel-Rahmène Azzouzi, M.D., Ph. D., Urology Service, CHU d’Angers; Stéphane Barrette, M.D., hematologist-oncologist, CHU Sainte-Justine; Louise Beaulac-Baillargeon, B. Pharm., Ph. D., Faculty of Pharmacy, Université Laval; Khaled Benabed, hematologist, CHU de Caen; Mehdi Benkhadra, Department of Anesthesia, Le Bocage Hospital, Dijon; Céline Bergeron, M.D., FRCPC, MSC, pneumologist, Université de Montréal Hospital Center; Christina Blais, Dt. P., M. Sc., Department of Nutrition, Université de Montréal; Pierre Blondeau, Ophtalmology Service, CHU de Sherbrooke; Gilles Boire, M.D., M. Sc., Rhumatology Service, Université de Sherbrooke; Andrée Boucher, M.D., endocrinologist, Université de Montréal Hospital Center; Mickael Bouin, M.D., Ph. D., gastroenterologist, Université de Montréal Hospital Center; Guylain Boulay, Ph. D., Department of Pharmacology, Université de Sherbrooke; Sylvain Bourgoin, Ph. D., Department of Anatomy-Physiology, Université Laval; André Cantin, M.D., Faculty of Medicine, Université de Sherbrooke; Michel Cayouette, Ph. D., Research Unit on Cellular Neurobiology, Institut de recherches cliniques de Montréal; Fatiha Chandad, Ph. D., Faculty of Dentistry, Université Laval; Bernard Cortet, Department of Rhumatology, CHU de Lille; Olivier Dereure, M.D., Ph. D., Dermatology Service, Université de Montpellier I; Serge Dubé, M.D., F.R.C.S.C., general surgeon, Maisonneuve-Rosemont Hospital, Montréal; Jean-Jacques Dufour, M.D., Otorhinolaryngology Service, Université de Montréal Hospital Center and Jewish General Hospital; Louis-Gilles Durand, O.Q., Ph. D., Ing., Biomedical Engineering Laboratory, Institut de recherches cliniques de Montréal; Wael El Haggan, M.D., nephrologist, CHU de Caen; Martin Fortin, Department of Family Medicine, Université de Sherbrooke; Jean-Marc Frapier, cardiovascular surgeon, CHU de Montpellier; Catherine Fressinaud, M.D., Ph. D., neurologist, CHU d’Angers; Dominique Garrel, Department of Nutrition, Université de Montréal; Serge Gauthier, M.D., FRCPC, McGill Centre for Studies in Aging; Franck Geneviève, M.D., Hematology Laboratory, CHU d’Angers; Jérémie Gerard, Hematology Laboratory, CHU d’Angers; Philippe Geslin, Cardiology Service, CHU d’Angers; Marc Girard, M.D., CHU Sainte-Justine; Philippe Granier, Nuclear Medicine Service, Antoine Gayraud Hospital, Carcassonne; Daniel Grenier, Ph. D., Faculty of Dentistry, Université Laval; Pavel Hamet, M.D., Ph. D., FRCPC, FCAHS, Genic Medicine Service, Université de Montréal Hospital Center; Luc Hittinger, Federation of Cardiology, Henri Mondor Hospital, Créteil; Thierry Jeanfaivre, M.D., Department of Pneumology, CHU d’Angers; Francine Jolicoeur, Ph. D., Centre intégré du cancer du sein, Université de Montréal Hospital Center; Chantal Kohler, M.D., Ph. D., Department of Histology, Cytology and Embryology, Université Henri Poincaré, Nancy; Stéphane Labialle, Ph. D., Obstetrics Department, McGill University; Pierre Lalonde, M.D., psychiatrist, Université de Montréal; Bernard Lambert, M.D., gynecologist, Université de Montréal Hospital Center; Patrice Le Floch-Prigent, Laboratoire d’anatomie de l’UFR de Médecine, Paris; Tony Leroux, Ph. D., audiologist, Université de Montréal and Raymond-Dewar Institute; Gérard Lorette, Dermatology Service, CHU de Tours; Jean-Pierre Marie, M.D., Department of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Hôtel-Dieu de Paris; René Martin, Department of Family Medicine, Université de Sherbrooke; Marie-Anne Mayoux-Benhamou, M.D, Ph. D., Service of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Cochin Hospital, Paris; Hortensia Mircescu, M.D., Endocrinology Service, Université de Montréal Hospital Center; Michel Mondain, M.D., Ph. D., Université Montpellier I; Didier Mouginot, Ph.D., Faculty of Medicine, Université Laval; Georges Mourad, M.D., Nephrology and Graft, Lapeyronie Hospital, Montpellier; Nicole Normandin, Ph. D., School of Orthophony and Audiology, Université de Montréal; Luc L. Oligny, M. Sc, M.D., pathologist, CHU Sainte-Justine; Philippe Orcel, Secrétaire général de la Société française de rhumatologie; Farid Ouacel, orthopedic surgery and traumatology, CHU d’Angers; Pierre Pagé, M.D., cardiovascular surgeon, Sacré-Coeur Hospital and Montreal Heart Institute; Aleth Perdriger, M.D., Ph. D., Rennes Hospital; Daniel Picard, Department of Radiology, Oncology and Nuclear Medicine, Université de Montréal Hospital Center; Luc Picard, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Neuroradiology Service, CHU de Nancy; Claude Poirier, pneumologist, Université de Montréal Hospital Center; Jean-Pierre Raynauld, Ph. D., Department of Physiology, Université de Montréal; Eric Renard, M.D., Ph. D., Endocrine Diseases Service, CHU de Montpellier; Nathalie Renaud, O.D., optometrist; Jean-Paul Rocca, Ph. D., odontologist, CHU de Nice; Pierre Rochcongar, Biology and Sports Medicine Unity, CHU de Rennes; José Sahel, Hepato-Gastroenterology Service, La Conception Hospital, Marseille; Louis-Georges Ste-Marie, M.D., Bone Diseases Laboratory, Université de Montréal Hospital Center; Laurent Salez, Ph. D., immunologist, Scienscrib, Montréal; Thierry Six, gynecologist-obstetrician, CHU de Caen; Ann-Muriel Steff, Pharm. D., Ph. D., LAB Recherche inc.; Daniel Thomas, Heart Institute, Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, Paris; Hervé Trillaud, M.D., Ph. D., Diagnostic and Therapeutic Imagery Service, CHU de Bordeaux; Guy Vallancien, Université Paris Descartes; Elvire Vaucher, Ph. D., School of Optometry, Université de Montréal; Monique Vincens, M.D., Ph. D., endocrinologist and pharmacologist, Université Paris VII; Catherine Vincent, M.D., hepatologist, Université de Montréal Hospital Center. Extrait de la publication Introduction The Visual Dictionary of the Human Body is a family atlas for exploration of the major systems of the human body. This book presents a collection of high-definition images of different parts of the body, linked to terms in several languages. Complementary texts (introductions and sidebars) offer additional information on the characteristics and functions of all systems shown. Structure The book is divided into 14 major themes, each of which is preceded by a two-page spread with a short text introducing the context. Within each theme, titles and subtitles classify the illustrations into subcategories, which makes it easier to find them in the table of contents. The book also has a glossary of 45 common anatomical terms and an index containing all of the terms, titles, illustration titles and subtitles used in the book. TITLE Titles are located at the top of the page, with the other languages below. If a title continues on more than one page it is grayed out on subsequent pages. human cell célula F humana Basic unit of the human body, whose size and shape vary depending on the functions that it performs. structure of a cell estructura F de la célula F All human cells have a similar structure: they are formed of a nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm and encased in a membrane. CELL AND TISSUES THEME The themes correspond to the systems and divisions of the human body. They are presented on each page in the edition’s main language. cell nucleus núcleo M celular Central core of the cell containing genetic information in the form of DNA and guiding protein synthesis. cytoplasm citoplasma M Liquid substance forming the inside of the cell, around the nucleus, in which cellular organelles bathe. endoplasmic reticulum retículo M endoplásmico Cell structure consisting of a network of pockets surrounding the nucleus; it is involved in protein synthesis. Golgi apparatus aparato M de Golgi Cell structure consisting of a group of membrane sacs; it is involved in the transport and maturation of proteins in the cell. microfilament microfilamento M Rod-shaped structure supporting the cell and giving it its shape. centriole centríolo M Cell structure playing a key role during mitosis. DEFINITION It explains the inherent qualities, function or characteristics of the element depicted in the illustration. TERM Each term is included in the index, with reference to the pages on which it appears. All the terms in the book were carefully selected following analysis of recent, high-quality documentation. vacuole vacuola F Spherical cavity in which water, waste and various substances required by the cell are stored. mitochondrion mitocondria F Structure associated with cell breathing; it produces and stores energy in the cell. ILLUSTRATION The extremely realistic illustrations contribute to the visual definition of the terms associated with them. pseudopod pseudópodo M Extension of the cytoplasm of certain cells, serving mainly in cell displacement. ribosome ribosoma M Organelle, floating free or bound to the endoplasmic reticulum, producing proteins essential to the formation and functioning of the human body. cell membrane membrana F celular microtubule microtúbulo M Cylindrical structure supporting the cell and allowing organelles and substances in the cell to move about. Bilayer of lipid molecules forming the outer surface of the cell. GENDER INDICATION F: feminine M: masculine N: neutral The gender of each common noun is indicated for the languages in which such categories exist. lipids lípidos M Molecules containing fatty acids, making up the cell membrane. The Life of Cells Each human being is composed of more than 50 trillion cells. Hundreds of millions of them die every minute, and just as many are born through cellular division. Some, such as certain white blood cells, die after only a few hours, while others, such as neurons, may survive throughout a human being's life. protein proteína F Organic compound formed of amino acids; in the cell membrane, proteins form channels allowing the exchange of substances with the outside environment. L Extrait de la publication SIDEBAR Sidebars present unusual or surprising facts that complement the information in each section. Contents Cell and tissues 6 human cell tissue mitosis DNA 8 10 12 13 Morphology 14 man woman 16 18 Skeleton 20 bones main bones skull vertebral column thoracic cage pelvis hand foot Muscles muscle main muscles head and neck thorax and abdomen upper limb lower limb Joints main joints cartilaginous joints synovial joints Nervous system structure of nervous system neuron nerve impulse nervous tissue central nervous system peripheral nervous system Cardiovascular system blood blood circulation blood vessels heart Lymphatic system organs of the lymphatic system Digestive system organs of the digestive system mouth teeth digestive tract pancreas liver 22 24 26 28 30 31 32 33 Respiratory system 34 Reproductive system 36 38 40 41 42 44 46 48 49 50 56 58 59 60 60 61 67 72 74 76 77 82 organs of the respiratory system upper respiratory tract lungs Urinary system organs of the urinary system urinary bladder kidney male genital organs female genital organs Sense organs sight hearing smell taste touch 84 86 88 90 91 92 94 97 98 100 102 103 105 108 110 111 112 114 116 118 122 124 128 130 132 134 Endocrine system 138 endocrine glands thyroid gland hypophysis suprarenal gland 140 141 142 143 Glossary Index 144 145 8 10 12 13 human cell tissue mitosis DNA Extrait de la publication Cell and tissues The human body is formed of hierarchically organized components (tissues, organs, and systems), of which the basic unit is the cell. Cells are the site of intense activity: they accumulate and transmit energy, make proteins that are essential to the body’s functioning, and constantly reproduce by cellular division. They also contain all of the genes belonging to each individual. Extrait de la publication human cell célula F humana Basic unit of the human body, whose size and shape vary depending on the functions that it performs. structure of a cell estructura F de la célula F CELL AND TISSUES All human cells have a similar structure: they are formed of a nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm and encased in a membrane. cell nucleus núcleo M celular Central core of the cell containing genetic information in the form of DNA and guiding protein synthesis. cytoplasm citoplasma M Liquid substance forming the inside of the cell, around the nucleus, in which cellular organelles bathe. endoplasmic reticulum retículo M endoplásmico Cell structure consisting of a network of pockets surrounding the nucleus; it is involved in protein synthesis. Golgi apparatus aparato M de Golgi Cell structure consisting of a group of membrane sacs; it is involved in the transport and maturation of proteins in the cell. microfilament microfilamento M Rod-shaped structure supporting the cell and giving it its shape. centriole centríolo M Cell structure playing a key role during mitosis. vacuole vacuola F Spherical cavity in which water, waste and various substances required by the cell are stored. mitochondrion mitocondria F Structure associated with cell breathing; it produces and stores energy in the cell. pseudopod pseudópodo M Extension of the cytoplasm of certain cells, serving mainly in cell displacement. ribosome ribosoma M Organelle, floating free or bound to the endoplasmic reticulum, producing proteins essential to the formation and functioning of the human body. cell membrane membrana F celular microtubule microtúbulo M Cylindrical structure supporting the cell and allowing organelles and substances in the cell to move about. Bilayer of lipid molecules forming the outer surface of the cell. lipids lípidos M Molecules containing fatty acids, making up the cell membrane. The Life of Cells Each human being is composed of more than 50 trillion cells. Hundreds of millions of them die every minute, and just as many are born through cellular division. Some, such as certain white blood cells, die after only a few hours, while others, such as neurons, may survive throughout a human being's life. protein proteína F Organic compound formed of amino acids; in the cell membrane, proteins form channels allowing the exchange of substances with the outside environment. 8 human cell cell nucleus núcleo M celular Central core of the cell containing genetic information in the form of DNA and guiding protein synthesis. chromatin cromatina F Substance consisting of proteins and DNA contained in the nucleus; it is compressed into chromosomes during mitosis. nucleoplasm nucleoplasma M Liquid substance forming the inside of the nucleus of a cell and in which especially chromatin and nucleoli bathe. CELL AND TISSUES nuclear envelope envoltura F nuclear Membrane surrounding the nucleus. nucleolus nucléolo M Spherical body located inside the nucleus and playing a role in the synthesis of ribosomes. examples of cells ejemplos M de células F The human body has about 200 types of cells, having very different characteristics and appearance depending on the functions that they perform in the organism. ovum óvulo M spermatozoon espermatozoide M muscle fiber fibra F muscular Mature female reproductive cell produced by the ovary; after fertilization by a spermatozoon, it enables an embryo to develop. Mature and mobile male reproductive cell produced by the testis; the main constituent of sperm, its purpose is to fertilize the ovum. Contractile cell, constituent element of muscles. osteocyte osteocito M chondrocyte condrocito M fat cell adipocito M Mature cell, constituent element of bone tissue. Cell, constituent element of cartilage. Cell forming the essential component of adipose tissue and ensuring the synthesis, storage and release of lipids. photoreceptor fotorreceptor M neuron neurona F white blood cell glóbulo M blanco red blood cell glóbulo M rojo Cell found in the retina capable of capturing light rays and translating them into nerve signals. Cell of the nervous system allowing information to be carried in the form of electrical and chemical signals. Blood cell belonging to the immune system, thus playing an essential role in the body’s defenses. Blood cell that carries oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. 9 tissue tejido M All the cells that have a similar structure and perform similar or complementary functions. Four main cell types make up the frame of the organism: epithelial, connective, muscle and nervous. CELL AND TISSUES epithelium tejido M epitelial microvillus microvellosidad F Protrusion of the cell membrane that increases its surface. Tissue formed of cells organized in layers; it serves covering, secretory and protective functions. basal lamina lámina F basal Extracellular matrix anchoring epithelial cells to adjacent tissue. epithelial cell célula F epitelial Cell component of epithelial tissue. examples of epithelia ejemplos M de tejidos M epiteliales They include tissues that form the covering of all body surfaces and line inner cavities (mucous membranes, endothelia, epidermis), and glandular tissues that have secretory functions. exocrine gland glándula F exocrina All secretory cells producing secretions released outside the body; they consist especially of salivary and sweat glands. excretory duct canal M excretor Duct carrying secretions from the exocrine gland. secretory cell célula F secretora Epithelial cell specialized in the secretion of various substances useful to the body. mucous membrane mucosa F Damp epithelial tissue lining an open cavity of the body; the mucous membrane plays a role in absorption and secretion (mucus). epithelium tejido M epitelial Tissue formed of cells organized in layers; it serves covering, secretory and protective functions. mucous gland glándula F mucosa Exocrine gland that secretes mainly mucus. mucus mucosidad F Translucent viscous substance secreted by the mucous membrane and that plays a protective role. mucous cell célula F calciforme Epithelial cell that secretes mucus. chorion corion M Loose connective tissue beneath the epithelial tissue of the mucous membrane. muscularis mucosae mucosa F muscular Fine layer of smooth tissue beneath the chorion. submucosa submucosa F Connective tissue beneath the mucous membrane. 10 tissue fibrous tissue tejido M fibroso Connective tissue characterized by an abundance of collagen fibers; it forms especially the tendons and ligaments. examples of connective tissues ejemplos M de tejidos M conjuntivos Connective tissue: tissue made up of relatively few cells and fibers bathed in a more or less abundant fluid; its functions are to support, protect and fill in spaces. CELL AND TISSUES adipose tissue tejido M adiposo Connective tissue made up essentially of adipocytes; it is the body’s energy reserve. cartilage tejido M cartilaginoso Connective tissue consisting of cells encased in a rigid substance; it covers the articular surfaces of bones and forms certain soft parts of the body. The Most Abundant elastic tissue tejido M elástico Connective tissue made up predominantly of elastic fibers; it is found especially in certain ligaments and in the walls of the arteries, trachea and vocal chords. Connective tissue, present in all organs, is the most abundant tissue in the human body: it accounts for two thirds of the total volume of tissue. 11 Extrait de la publication mitosis mitosis F All the mechanisms of cell division that allow the formation of two identical daughter cells from a mother cell. CELL AND TISSUES prophase profase F First stage of mitosis, during which the chromatin condenses into chromosomes; the two pairs of centrioles move toward opposite poles. interphase interfase F metaphase metafase F Period between two successive cell divisions, during which the cell grows. Second stage of mitosis, during which the chromosomes align in the middle of the cell, guided by the mitotic spindle; the nuclear membrane disaggregates. chromosomes cromosomas M Elements of the nucleus of a cell, made up of DNA and proteins and carrying genetic information; they are observed only during cell division. centrioles centriolos M Double cellular structures that duplicate during interphase. mitotic spindle huso M mitótico Ephemeral cellular structure joining the two pairs of centrioles during mitosis. cytokinesis citocinesis F anaphase anafase F Stage of mitosis during which the cytoplasm separates in two; the original cell (or mother cell) is replaced by two identical daughter cells. Third stage of mitosis, during which the chromosomes separate into chromatids and move to either of the cell’s poles. telophase telofase F Fourth stage of mitosis, during which the chromosomes reassume the appearance of the chromatin; a new nuclear envelope appears to cordon off the two nuclei. chromatid cromátida F One of the two strands of a chromosome. cytoplasm citoplasma M Gel-like substance forming the inside of the cell, around the cell nucleus. 12 Extrait de la publication DNA ADN M Complex molecule containing the genetic characteristics (genes) of every person. DNA molecule molécula F de ADN M Billions of Copies adenine adenina F Complementary nitrogenous base of thymine. thymine timina F Complementary nitrogenous base of adenine. nucleotide nucleótido M cytosine citosina F Complementary nitrogenous base of guanine. Basic unit of DNA molecules, consisting of a nitrogenous base. guanine guanina F Complementary nitrogenous base of cytosine. nitrogenous base base F nitrogenada Small constituent molecule of a nucleotide; there are four types that assemble in the DNA molecule to form a sequence specific to each individual. chromosomes cromosomas M Elements of the nucleus of a cell, made up of DNA and proteins and carrying genetic information; they are observed only during cell division. autosome autosoma M Chromosome that carries hereditary characteristics unrelated to sex. sex chromosomes cromosomas M sexuales Chromosomes responsible for determining sex. centromere centrómero M Short section of a chromosome that holds the two chromatids together. X chromosome cromosoma M X Sex chromosome present in both men and women. Y chromosome cromosoma M Y Sex chromosome present only in men. chromatid cromátida F One of two strands of a chromosome, consisting of a short arm and a long arm; during cell division, the two chromatids separate at the centromere. 13 Extrait de la publication CELL AND TISSUES The DNA molecule appears in the shape of a double helix made up of billions of nucleotides; it is the largest molecule in the human body. The human genetic heritage is included in 46 chromosomes (22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes). Each cell in the body has its own copy: for example, a skin cell contains the instruction for eye color. 16 18 man woman Morphology The human body is divided into four main anatomical regions: the head, which contains the main sensory organs; the trunk, which contains most of the internal organs; the upper limbs, which provide gripping ability; and the lower limbs, which allow for locomotion and an upright posture. These parts are linked to each other by complex joints, which enable them to make independent and very complex movements. Extrait de la publication man hombre M Human being of the male sex whose skeleton is generally larger and heavier than that of the female; he produces cells able to fertilize the ovum. MORPHOLOGY man: anterior view hombre M: vista F anterior face rostro M Front part of the head. forehead frente F Upper part of the face between the eyebrows, hairline and temples. temple sien F Side of the head between the forehead, eye, cheek and ear. chin barbilla F Protruding part of the lower face, corresponding to the mandible. cheek mejilla F Side of the face containing muscles capable of giving it many different expressions. shoulder hombro M Joint connecting the arm with the thorax. mouth boca F Initial part of the digestive tube made up of a cavity (oral cavity) surrounded by lips; it allows the ingestion of food and plays a role in tasting, speaking and breathing. armpit axila F Hollow located beneath the shoulder between the arm and thorax and covered with hair at puberty. Adam's apple nuez F Protrusion of men’s necks, formed by the joining of two strips of cartilage from the larynx. breast seno M Front part of the thorax containing the nipple; in men, the breast is barely developed and plays no particular role. thorax tórax M Upper part of the trunk, above the diaphragm, containing especially the heart and lungs. navel ombligo M Scar in the form of a rounded depression resulting from the cutting of the umbilical cord. abdomen abdomen M Lower part of the trunk, beneath the diaphragm, containing the main organs of the digestive, urinary and reproductive systems. hand mano F Terminal part of the upper limb having a tactile and prehensile function. penis pene M Erectile organ of men allowing copulation and voiding of urine. groin ingle F Depression located at the junction of the abdomen and thigh. knee rodilla F Joint connecting the thigh with the leg. ankle tobillo M Joint connecting the foot with the leg. Average Size foot pie M Terminal part of the lower limb, resting on the ground during upright stance. The height of adult men varies enormously from one individual to another (between 1.40 m and 2 m on average). Aside from genetics, a number of factors influence growth, including environment, behavior, and diet. toe dedo M del pie M Extension of the foot, made up of several articulated bones (phalanges) and whose terminal end is covered with a nail. 16 Extrait de la publication man man: posterior view hombre M: vista F posterior neck cuello M Part of the body joining the head to the trunk and containing especially the cervical vertebrae and larynx. ear oreja F Organ of hearing and balance made up of three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. MORPHOLOGY head cabeza F Upper part of the body, supported by the neck and containing the main sensory organs and brain. nape nuca F Hind part of the neck made up mainly of muscles. back espalda F Hind part of the thorax. trunk tronco M Part of the body formed by the thorax and abdomen, to which the head and limbs are attached. arm brazo M Part of the upper limb between the shoulder and elbow, corresponding to the humerus. elbow codo M Joint between the arm and forearm, formed by the lower extremity of the humerus and the upper extremities of the radius and ulna. forearm antebrazo M Part of the upper limb between the elbow and wrist. wrist puño M Joint connecting the hand with the forearm. thigh muslo M Part of the lower limb between the hip and knee, corresponding to the femur. hip cadera F Joint connecting the leg with the pelvis. buttocks nalgas F Fleshy parts located beneath the lumbar region, made up mainly of muscles. leg pierna F Part of the lower limb between the leg and ankle. little finger meñique M Fifth and smallest digit of the hand. calf pantorrilla F Hind part of the leg, made up of triceps surae. ring finger anular M Fourth digit of the hand; rings are traditionally worn on this finger, hence its name. middle finger corazón M Third and longest digit of the hand. heel talón M Hind part of the foot, corresponding to the calcaneus. thumb pulgar M First digit of the hand, short and strong, opposable to the other digits to enable grasping. index finger índice M Second digit of the hand, often used to point, hence its name. 17 Extrait de la publication woman mujer F Human being of the female sex capable of conceiving children from an ovum fertilized by a spermatozoon. woman: anterior view mujer F: vista F anterior MORPHOLOGY forehead frente F Upper part of the face between the eyebrows, hairline and temples. face rostro M Front part of the head. mouth boca F Initial part of the digestive tube made up of a cavity (oral cavity) surrounded by lips; it allows the ingestion of food and plays a role in tasting, speaking and breathing. temple sien F Side of the head between the forehead, eye, cheek and ear. nose nariz F Protrusion in midsection of the face, with two orifices (nostrils), having an olfactory and respiratory function. cheek mejilla F Side of the face containing muscles capable of giving it many different expressions. chin barbilla F Protruding part of the lower face, corresponding to the mandible. armpit axila F Hollow located beneath the shoulder between the arm and thorax and covered with hair at puberty. thorax tórax M Upper part of the trunk, above the diaphragm, containing especially the heart and lungs. breast seno M Glandular organ rich in adipose tissue, enclosing the pectoral muscles and secreting milk to feed the newborn after birth. navel ombligo M Scar in the form of a rounded depression resulting from the cutting of the umbilical cord. abdomen abdomen M Lower part of the trunk, beneath the diaphragm, containing the main organs of the digestive, urinary and reproductive systems. vulva vulva F All the external female genital organs protecting the clitoris and vaginal opening. groin ingle F Depression located at the junction of the abdomen and thigh. knee rodilla F Joint connecting the thigh with the leg. little toe dedo M pequeño del pie M Last and smallest toe of the foot. fourth toe cuarto dedo M del pie M Toe located between the third toe and little toe. third toe tercer dedo M del pie M Toe located between the second toe and fourth toe. second toe segundo dedo M del pie M Toe located between the big toe and third toe. ankle tobillo M Joint connecting the foot with the leg. big toe dedo M gordo del pie M First and largest toe of the foot. 18 Extrait de la publication foot pie M Terminal part of the lower limb, resting on the ground during upright stance. Índice español vesícula sináptica 60 vestíbulo 129 vías respiratorias superiores 103 vías respiratorias superiores, sección 104 vibraciones sonoras 129 visión, mecanismo 126 vista 124 vista, defectos 127 vómer 27 vulva 18 Y yema gustativa 133 yeyuno 95 yunque 129 Z zona fasciculada 143 zona glomerulada 143 zona reticulada 143 160 Extrait de la publication Human Bod of the English definitions visuAly S PA NISH The Visual Dictionary of the Human Body offers a unique look at that wonderful machine that is the body. From head to toe, spectacular, high-definition images created with the most up-to-date imagery technology offer exceptional views of all major body parts. Precise terminology in two languages, together with definitions and complementary texts, allow readers to go beyond the images and acquire knowledge of the special characteristics and workings of the different anatomical systems. Attractive, entertaining, and educational: the Visual Dictionary of the Human Body is an indispensable family reference, and a great tool to acquire vocabulary and discover the complexity of the human body. 1,500 terms 250 highly realistic illustrations lungs upper respiratory tract pulmones M Organs of the respiratory system made of elastic tissues and responsible for the exchange of gases between the air and the blood. frontal sinus seno M frontal Cavity in the frontal bone, connecting with the nasal cavities and warming inhaled air. nasal cavity fosas F nasales Each of two cavities, separated by the nasal septum and opening in front through the nostrils and in back into the nasopharynx. Respiration An adult at rest breathes about 15 times a minute, or more than 21,000 times per day. With each inhalation, a half-liter of air loaded with oxygen passes through the respiratory tract to the lungs. sphenoidal sinus seno M esfenoidal Cavity in the sphenoid bone, connecting with the nasal cavities and warming inhaled air. soft palate paladar M blando Muscular membranous wall separating the nasopharynx and buccal cavity; it assists especially in food ingestion and vocalization. hard palate paladar M duro Bony separation between the buccal and nasal cavities, extended by the soft palate. mouth boca F Initial part of the digestive tube made up of a cavity (oral cavity) surrounded by lips; it allows the ingestion of food and plays a role in tasting, speaking and breathing. trachea tráquea F Muscular cartilaginous channel allowing air to pass between the larynx and bronchi. pharynx faringe F Muscular membranous channel joining the nasal cavities to the larynx as well as the buccal cavity to the esophagus; it serves as a passageway for air and food. tongue lengua F Muscular organ located in the buccal cavity and involved in tasting, chewing and talking. right lung pulmón M derecho Respiratory organ divided into three lobes, in which blood from the right pulmonary artery is freed of carbon dioxide and enriched with oxygen. vocal cords cuerdas F vocales Long bands of muscle tissue attached to the thyroid and arytenoid cartilages; their vibration allows sounds to be produced. epiglottis epiglotis F Mobile catilaginous lamina located in the upper part of the larynx, directing food to the esophagus at the moment of swallowing. larynx laringe F Muscular cartilaginous channel connecting the pharynx and trachea; it contains the vocal cords and has a vocalizing and respiratory function. thyroid cartilage cartílago M tiroides Connective tissue structure formed of two lateral laminae whose juncture, on the front part of the larynx, forms a highly visible protrusion in men (Adam’s apple). trachea tráquea F Muscular cartilaginous channel allowing air to pass between the larynx and bronchi. pharyngeal tonsil amígdala F faríngea Lymphoid organ located in the nasopharynx, filtering pathogens from the air. nasopharynx rinofaringe F Upper part of the pharynx connecting with the nasal cavities. oropharynx orofaringe F Median part of the pharynx connecting with the buccal cavity. RESPIRATORY SYSTEM RESPIRATORY SYSTEM sagittal section of upper respiratory tract sección F sagital de las vías F respiratorias superiores right superior lobe lóbulo M superior derecho Upper part of the right lung, separated from the inferior lobe and middle lobe by a horizontal fissure. middle lobe lóbulo M medio Part of the right lung, separated from the superior lobe and inferior lobe by an oblique fissure. right inferior lobe lóbulo M inferior derecho Lower part of the right lung, separated from the superior lobe and middle lobe by an oblique fissure. diaphragm diafragma M Muscle separating the thorax from the abdomen; its contraction increases the volume of the thoracic cage and lungs. left lung pulmón M izquierdo Respiratory organ divided into two lobes, in which blood from the left pulmonary artery is freed of carbon dioxide and enriched with oxygen. left superior lobe lóbulo M superior izquierdo Upper part of the left lung, separated from the inferior lobe by an oblique fissure. heart corazón M Muscular organ divided into four chambers whose autonomous rhythmic contractions cause blood to circulate throughout the body. oblique fissure cisura F oblicua Fissure separating the lobes of the lung. left inferior lobe lóbulo M inferior izquierdo Lower part of the left lung, separated from the superior lobe by an oblique fissure. pleura pleura F Elastic membrane surrounding each lung and composed of two layers bounding the pleural cavity. laryngopharynx laringofaringe F Lower part of the pharynx connecting with the larynx and esophagus. hyoid bone hueso M hioides Bone supporting the larynx and serving as an insertion for various muscles of the tongue, pharynx and larynx. 10 104 Topics Cell and Tissues Lymphatic System Morphology Digestive System Skeleton Respiratory System Muscles Urinary System Joints Reproductive System Nervous System Sense Organs Cardiovascular System Endocrine System Extrait de la publication All images and texts have been verified by a scientific committee made up of 300 medical experts and university professors.