* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pituitary Adenoma Diagnosis and Management Anatomical land
Survey
Document related concepts
Vasopressin wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Sex reassignment therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (menopause) wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Graves' disease wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
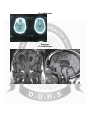
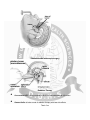
Pituitary Adenoma Diagnosis and Management Anatomical land marks Suprasellar space Anteriorly Laterally Posteriorly Inferiorly Superiorly - Tuberculum sella - Medial temporalLobes - Brain stem - Diaphragm sella - Basifrontal lobes Pituitary Gland ( pituitary/ hypophysis Cerebri ) Lies in pituitary fossa in sphenoid bone. Adenohypophysis Neurohypophysis A horizontally placed ovoid • • • • Transverse body 12-15mm Ant:post: 8-10mm Height 5-7mm Weight 0.5-0.7gm 0.8-1gm (Pregnant lady) - Anterior pituitary - Posterior pituitary Function of Pituitary Gland • • • Regulates the function of thyroid glands, the adrenal glands, ovaries and testes Controls the lactation, uterine contractions during labor and linear growth and it regulates the osmolality and intravascular fluid, through kidneys. Comprised of anterior and posterior lobes. • • Eight peptide hormone, two from posterior and six from anterior. Disorders, causing s/s are due to, • • • (i) excess or deficient hormone secretion (ii) extrinsic compression (iii) interruption of blood supply. Pituitary hormones ANTERIOR PITUITARY Adrenocorticotropin Thyroid stimulating hormone Follicle stimulating hormone Leutinizing hormone Growth hormone Prolactin ACTH TSH FSH LH GH PRL POSTERIOR PITUITARY Antidiuritic hormone Oxytocin ADH Clinical assessment Assessment of pituitary function: Clinical evaluation for hormonal deficiency or excess. Laboratory testing of the various pituitary- target organ axes. Endocrine evaluation confirms endocrinopathy and help in establishing the diagnosis. Endocrine values may be used as prognostic index for those going under the treatment, surgery or radiation therapy. Pituitary tumors Pituitary tumors • Benign • • • • Malignant Pituitary tumors Benign tumors are:- Non secretary Secretary 1-Prolactinoma 2-Growth hormone secretary tumors 3-ACTH secretary tumors 4-Others Epidemiology of pituitary adenoma • • • • • • 10% of all intracranial tumors Most common in 3rd and 4th decade of life Equally affect both sexes Clinical presentation of pituitary tumors Mass Effects Endocrinological disturbances Clinical presentations Mass Effects Visual disturbance(bi-temporal hemianopsia,) Obstructive hydrocephalus Pituitary apoplexy and ischemia Clinical presentations • Hypersecretions of a particular hormones The symptoms depends upon the hormonal secretions. Include variety of symptoms and signs FUNCTIONAL PITUITARY TUMORS • • • • • • The most common functional pituitary tumors secrete one of the following: 1-prolactin (PRL): prolactinomas are the most common secretory adenoma. Causes amenorrheagalactorrhea syndrome (AKA Forbes-Albright syndrome, AKA Ahumada-del Castillo syndrome) in females, impotence in males, and often infertility in either sex. Also causes bone loss FUNCTIONAL PITUITARY TUMORS 2-adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH): AKA corticotropin. This is Cushing's disease. Elevated ACTH causes either: A. endogenous hypercortisolism (Cushing's disease B. Nelson's syndrome: hyperpigmentation (due to melanin stimulating hormone (MSH) cross reactivity with ACTH). Develops in 10·30% of patients who have undergone adrenalectomy for treatment of Cushing's syndrome FUNCTIONAL PITUITARY TUMORS • • • 3-Growth hormone (GH): causes acromegaly in adults (see below). In prepubertal children (before epiphyseal closure), it produces gigantism (very rare) FUNCTIONAL PITUITARY TUMORS • Rare pituitary adenomas secrete: • • 1-Thyrotropin (TSH): produces thyrotoxicosis 2-Gonadotropins (leutinizing hormone (LH) andlor follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)): usually does not produce a clinical syndrome Diagnostic tools • • • • Radiology:- CT scan, MRI Scan with pituitary protocol Visual perimetery Hormonal quantitative assessment Histopathology Radiology X-Ray Skull lateral view Radiology CT and MRI scans Radiology CT and MRI scans Visual Perimetery Hormonal Assessment • • • May give indication of tumor type May indicate the need of hormonal replacement if there is any deficiency preoperatively. May serve as a baseline to compare with post operative deficiency. Hormonal assessment Endocrinological Screening 1-8 Am serum cortisol level 2-Serum Prolactin levels 3-T4 and TSH levels 4-Somatomedin-c(IGF-1 level) 5-Fasting Blood Glucose Hormonal Assessment • Detailed Hormonal assessment of a particular pituitary axis depends upon history physical examination and results of hormonal screening. Management • Medical – – Replacement of deficient hormones Treatment of some functional tumors such as Prolactinomas and GH tumors • • Surgical – – Functioning tumors such as Acromegaly, Cushing’s, Prolactinomas Non-functioning tumors Visual effects & Hypopituitarism, Radiotherapy / Radiosurgery Medical Management • • Prolactinoma:- Most of the prolactinomas are treated by drugs including:1-Dopamine Agonist like Bromocriptine(Parlodel),pergolide,cabergoline Growth Hormone secretary adenoma:1-Dopamine agonist 2-Pegvisomant(competitive GH recep Antagonist) 3-Octerotide(GH secretion suppressor) Rationale For Surgical Management • • • Apart from cosmetic considerations, patients with active Acromegaly are unhealthy, and their life span is shortened significantly. Unless treated successfully by either medical or surgical means, Prolactinomas have consequences that are profound for physical and psychological health as well as fertility. Cushing’s disease becomes disabled rapidly by a range of cortisol produced complications, and a shortened life expectancy is a certain consequence of uncontrolled hypercortisolism. Goals Of Surgery For Pituitary Adenomas Surgical Approaches Endoscopic Transsphenoidal endoscopic surgery Radiation Therapy • • Conventional XRT usually consists of 40-50 Gy administered over 4-6 weeks. Gamma Knife:-is better mode of radiation therapy with less side effects Thank You