* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Functional Characterization of Soybean Transcription Factor
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
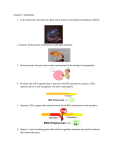
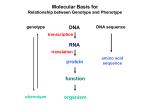
Functional Characterization of Soybean Transcription Factor GmbZIPE2 Gonçalves, A.B.; Alves, M.S.; Dadalto, S.P.; Fietto L.G. Dep. de Bioquímica e Biologia Molecular, UFV, Viçosa, MG, Brazil. INTRODUCTION: Transcription factors are proteins that regulate gene expression by binding to specific sequences in DNA. Transcription factors are among the major targets to increase the tolerance of plants to stresses, since these proteins control the expression of several genes simultaneously. Members of the bZIP family of transcription factors are characterized by having a leucine zipper domain which is a basic DNA binding domain. Previous research demonstrated that the GmbZIPE2 gene in soybean (Glyma05g30170.1) is responsive to pathogens . OBJECTIVES: The objective of this study was functionally characterize the transcription factor GmbZIPE2, by discovering which promoters binds to it, as well as determining their possible modulation of target genes. MATERIAL AND METHODS: In this research, GmbZIPE2 was amplified and cloned into a bacterial expression vector (pDEST17) and this was inserted into Escherichia coli strain C41 in which the recombinant protein was successfully expressed. The GmbZIPE2 protein was used in electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) using two cis-elements related to defense against pathogens, H-box and G-box. qRT-PCR experiments were performed to establish the relationship between the overexpression of GmbZIPE2 and expression of genes related to plant defense against pathogens. RESULTS: Our results demonstrated that GmbZIPE2 binds to H-box, but does not bind to the G-box. It was found that overexpression of GmbZIPE2 in soybean protoplasts does not interfere with the expression of GmPAL-1 and GmOMT (genes encoding proteins related to the biosynthesis of lignin and phenylpropanoid), but it activates the expression of pathogenesis-related gene 1 (GmPR1) gene which expression is induced in response to a variety of pathogens. CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that GmbZIPE2 modulates the expression of genes related to defense against pathogens in plants. Word Keys: biotic stress, bZIP, Glycine max Supported by: CAPES, CNPq and FAPEMIG