* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lactanase - Vita Flex
Survey
Document related concepts
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
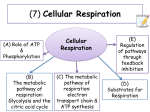
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
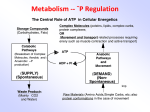
Lactanase ® Supplies nutrients important for the formation of acetyl coenzyme A, the gateway to efficient release of cellular energy • Special combination of riboflavin, pantothenic acid, thiamine, niacin and lipoic acid • • • • Helps cells efficiently deliver fuel from anaerobic metabolism to the Krebs cycle for energy release Contains the key nutrients needed to release energy from both carbohydrates and fats A favorite of Thoroughbred and Standardbred trainers and veterinarians Easily absorbed, so it can be given shortly before performance for extra metabolic power What Is Lactanase? Lactanase supplies nutrients important for the formation of acetyl coenzyme A in the horse's body. Acetyl coenzyme A is the gateway to the Krebs cycle, where the release of cellular energy takes place. This formula was the first pre-performance supplement to focus on the need for acetyl coenzyme A during intensive exercise, when the horse cannot rely upon oxygen for energy release. Lactanase has been tested by Thoroughbred and Standardbred trainers and veterinarians at the nation's leading racetracks. It is now available to all horsemen for optimum support of horses involved in intensive exercise and performance. Anaerobic Metabolism is Used To Maintain Intensive Exercise When horses perform or exercise intensely, they quickly face a demand for energy that is greater than the amount of oxygen available to produce it. When more than half of the horse's energy is produced without oxygen, the horse is performing anaerobically. Anaerobic metabolism typically begins to dominate after galloping only one-quarter of a mile, and for many horses it kicks in sooner. Lactanase addresses some of the fundamental nutritional needs of anaerobic metabolism to provide targeted support for high-intensity equine athletes. The Bridge to ATP D-Glycogen is the main energy source for intensive exercise that lasts more than a few seconds. It is converted through many steps to enter the Krebs cycle to produce ATP, the basic biological energy source. In the anaerobic metabolism of intense exercise, these steps must be made without additional oxygen. A crucial junction is the conversion of pyruvate (from glycogen) to acetyl coenzyme A, where it enters the Krebs cycle. If the cell lacks the necessary nutrients to form acetyl coenzyme A, pyruvate will be changed into lactic acid (lactate). Lactic acid must be reconverted or transported to the liver for processing through the Cori cycle. Researchers point to the buildup of lactic acid in the blood and within the muscle cells as a possible indication of fatigue and inability of the cells to produce energy and control muscle function. The Essential Co-Factors And The Lactanase Formula Lactanase supplies nutrients that serve as substrates of key enzymes needed for the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A. Thiamine, also known as vitamin B1, forms thiamine pyrophosphate, or TPP, a coenzyme used to begin pyruvate conversion. Lipoic acid is a sulfur-bearing fatty acid that is produced within the body, and is also found in low levels in yeast, liver and other foods. Lipoic acid's unique arrangement of electrons gives it a key role in the synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A. Pantothenic acid, sometimes called vitamin B5, is a major building block of acetyl coenzyme A. Riboflavin, or B2, is the basis of an enzyme called FAD, and niacinamide (a form of vitamin B3) is used to produce NAD, a coenzyme. These are the nutrients supplied by Lactanase. Together they help the cells to efficiently deliver fuel from anaerobic metabolism to the Krebs cycle for energy release. Because the horse can quickly and easily absorb these nutrients, Lactanase can be given shortly before performance to provide extra metabolic power when you really need it. Bonus: Lactanase And The Metabolism Of Fats One of the main pathways to release energy from fats produces a fatty acid called alpha-ketoglutarate. Like pyruvate, alpha-ketoglutarate must cross a crucial bridge before it can be used in the Krebs cycle. Thiamine, lipoic acid, pantothenic acid and niacinamide support the enzymes that get the job done. Lactanase does double duty with key nutrients the horse needs to release energy from both carbohydrates and fats. Feeding Instructions: Blend thoroughly with feed. For support under stressful conditions, feed one packet daily for two days. Thereafter feed one-half to one packet as needed. For performance support, feed one packet 2 to 3 hours prior to performance. For maximum support, feed one additional packet the evening before performance. © 2005 Vita Flex Nutrition

![NEC313N, ACETYL COENZYME A, [ACETYL-1- C]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003392842_1-f84d6512b3156ee480c7453e33ca6834-150x150.png)