* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1: Value and Magnitude of Rational Numbers
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli number wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
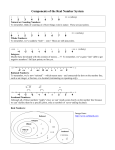
Unit 1: Value and Magnitude of Rational Numbers
TEKS:
8.2A(S) extend previous knowledge of sets and subsets using a visual
representation to describe relationships between sets of real numbers
(irrational numbers are introduced in Unit 8)
8.2D(R) order a set of real numbers arising from mathematical and
real-world contexts
8.2C(S) convert between standard decimal notation and scientific
notation (irrational numbers are introduced in Unit 8)
Vocabulary
Base: the number in an expression or equation which is raised to a power or exponent
Counting (natural) numbers: the set of positive numbers that begins at one and increases by increments of one each
time {1, 2, 3, …, n} – how you naturally count
E: a symbol used in a calculator to indicate that the preceding number should be multiplied by ten raised to the number
that follows
Integers: the set of counting (natural) numbers and their opposites {-n, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, …, n}
Powers: denoted by a number or variable in the superscript place of the base which designates how many times the
base will be multiplied by itself if it is positive, or by its inverse if it is negative
𝑎
Rational numbers: the set of numbers that can be expressed as a fraction 𝑏, where a and b are integers and b ≠ 0;
includes subsets of integers, whole numbers, and counting numbers.
Scientific notation: a representation of a number by using a method to write very large or very small numbers using
powers of ten that is written as a decimal with exactly one nonzero digit to the left of the decimal point multiplied by a
power of ten
Whole numbers: the set of counting (natural) numbers and zero {0, 1, 2, 3, …n}