* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is LDO (Low-Dropout Voltage Regulator) 2006/6 John Wu 吳旻翰
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
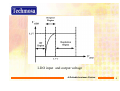
What is LDO (Low-Dropout Voltage Regulator) 2006/6 2006/6 John John Wu Wu 吳旻翰 吳旻翰 A Reliable business Partner 1 Agenda • • • • • What is LDO? Why use LDO? Major types of LDO How to select a LDO? Other design issue A Reliable business Partner 2 What is a LDO? VIDD: Input voltage VODD:Output voltage Basic LDO architecture A Reliable business Partner 3 Pass elements of LDO Transistor: PNP Transistor: Ic=β* Ib Ic=α*Ie α=β/(β+1) <1 NPN MOSFET: N-MOS P-MOS MOSFET: Working on resistive region ID = K[2(VGS-VT) VDS-VDS2 ] VT = threshold voltage K= conductance parameter A Reliable business Partner 4 LDO input and output voltage A Reliable business Partner 5 Why Linear? A Reliable business Partner 6 Why use LDO? Benefits : 9 Low cost & Easy-to-use 9 Accurate supply voltage 9 Active noise filtering 9 Protection from over-current faults 9 Generation of multiple output voltages from a Single source Fault: 9Efficiency is bed 9Thermal issue A Reliable business Partner 7 Why use LDO? Who Prefers LDO? 9 9 9 9 9 Communications equipment Small devices Battery operated systems Low current devices High performance microprocessors with sleep mode (fast transient recovery required) 9 Analog Device ( Audio power,RF power…) A Reliable business Partner 8 Major types of LDO (A) “Classic” NPN-based regulators that require 2.5 to 3V of excess input voltage to function.7805,317,340 (B) “Low Dropout NPN” regulators, with a NPN output but a PNP base drive circuit. These devices reduce the dropout requirement to 1.2 to 1.5V. (C) True low dropout PNP-based regulators that need 0.3V to 0.6V extra for operation. A Reliable business Partner 9 Major types of LDO (D) P-channel CMOS output regulators. These devices have very low dropout voltages at low currents but require large die area (hence higher costly than bipolar versions) (E) Regulator controllers. Provide the control functions of a linear regulator, and do not have the pass element on it. It provide the advantage of optimizing die area and cost for higher current applications. A Reliable business Partner 10 Major types of LDO 各種傳輸元件的效能比較 %各有優劣% A Reliable business Partner 11 How to select LDO? The most important parameters of LDO: • • • • • • • Input voltage (Vin) Output voltage (Vout) Maximum output current (Iout) Dropout voltage Ground current /quiescent current (Iq) Power disspation = (Vin-Vout) *Iout +Vin* Iq Package A Reliable business Partner 12 Other design issue Component selection: Input capacitor • Depends your Vin power quality. • Larger values may be required if Vin has high ripple. • X7R,X5R ceramic capacitor can be used for bypassing. Output capacitor • • • • • There is recommend minimum value of it. Compensation Low inductance, low ESR would be better. PNP&PMOS LDO need specified range ESR value. Exp: X7R,X5R,Tantalum A Reliable business Partner 13 Other design issue LDO Efficiency: Eff= Pout / Pin= Vout*Iout / Vin*Iin And , Iout ~= Iin A close efficiency approximation : Eff = Vout / Vin Power Supply Rejection Ratio(PSRR): PSRR(dB)=20Log(△ Vin/ △ Vout) A Reliable business Partner 14 Other design issue Thermal Management • LDO power dissipation and heat-sink requirements for various 3.3V current levels. • Θ Thermal resistance(C/W) Θ =△T/Q △T: Temperature difference Q : Power dissipation • Θ SA : Haet Sink to Ambient (free air) Thermal resistance • Ambient Temperature Affects Heat Sink Requirements A Reliable business Partner 15 Other design issue The minimum amount of copper can be determined by knowing the maximum power dissipation required. A Reliable business Partner 16 Other design issue What is a high performance LDO? 9 Wide Vin voltage range 9 Low Iq current 9 Low dropout voltage 9 Small output capacitor 9 High PSRR 9 Over current protection 9 Fast Transient Response 9 Low Thermal resistance 9Small package A Reliable business Partner 17 Q&A Thank You ! A Reliable business Partner 18