* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Animations science.nhmccd.edu/biol/bio1int.htm
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
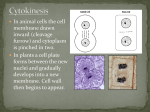
Cells The Basic Unit of Life, Reference, pages 13-23, McGraw-Hill Ryerson Organelles Special structures that perform specific functions in cells Cell Animations science.nhmccd.edu/biol/bio1int.htm Nucleus Has a double-layered porous (with pores - very tiny holes) membrane Contains DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), DNA forms chromatin (long strands) and has instructions to assemble the necessary substances for building the cell and making it work Has a nucleolus, a dark structure that manufactures ribosomes Cytoplasm The area outside the nucleus and inside the cell membrane. The cell membrane separates the cell contents from its surroundings. Jelly-like material Supports nucleus and other organelles Ribosomes Structures that make protein Protein is used to make enzymes, muscle tissue, and other important structures Endoplasmic Reticulum Series of canals Canals are used to transport materials to different parts of the cells Rough Endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes attached Mitochondria Transform energy for the cell Golgi Bodies Package useful materials and secrete them to the outside of the cell for use elsewhere Vacuoles Fluid-filled storehouses that contain water, food, wastes and other materials Lysosomes Break down food and digest wastes and worn out cell parts The Cell Cycle Cell division allows organisms to grow and develop When cells divide, they must have a complete nucleus, so all the instructions in the DNA are reproduced The process that makes this happen is MITOSIS Before Mitosis Cells copy the chromatin so there are two sets of DNA The chromatin coils up to form double-stranded chromosomes, joined by a centromere Copy Figure 1.9 on page 17 Phases of Mitosis Remember PMAT Four major phases Results in two complete sets of DNA Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase Prophase Chromosomes visible with a microscope Nuclear membrane disappears Spindle fibres form and stretch across the cell Spindle fibres attach to centromeres Metaphase Spindle fibres pull chromosomes into a line across the middle of the cell Anaphase Spindle fibres shorten Centromeres are pulled apart Chromosomes move to the opposite (ends) poles of the cell Telophase Final phase of mitosis Spindle fibres disappear Nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromosomes Nucleolus appears Single stranded chromosomes uncoil into strands of chromatin The cell is ready to divide-cytokinesis Cell Division After telophase Animal cells - the membrane pinches together and the cell divides Plant cells - a cell plate develops across the centre of the cell forming a new cell wall Two new cells- daughter cells Number of chromosmes in the nucleus of each cell is identical to the number in the original cell Interphase Inter- between Cell growth, replication of DNA Prepares for mitosis Refer to the cell cycle pie graph on page 23 Mitosis is ____ h Rapid growth is ____ h Growth and DNA replication is ____h Growth and preparation for division is ____ h Sketch the phases of Mitosis to go with your explanations. Do questions 3 and 4, page 16; 1-7 on page 23.