* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DC Voltage and Current Sources
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
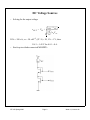
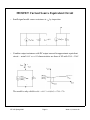
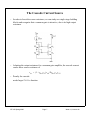
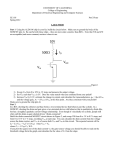
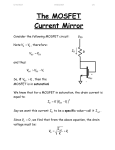
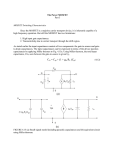
DC Voltage and Current Sources * Output characteristics of a BJT or MOSFET look like a family of current sources ... how do we pick one? specify the gate-source voltage VGS in order to select the desired current level for a MOSFET ( specifiy VBE exactly for a BJT) how do we generate a precise voltage? ... we use a current source to set the current in a “diode-connected” MOSFET note that this is a “one-port” ... NOT an amplifier! (wait a minute ... where do we find IREF? Assume that one is available!) 2 W i D = I REF + i OUT ≅ ------ µ C ox ( v OUT – V Tn ) 2L n EE 105 Spring 2000 Page 1 Week 11, Lecture 26 DC Voltage Sources * Solving for the output voltage I REF + i OUT v OUT = V Tn + -----------------------------W ------ µ C 2L n ox If ID = 100 µA, µn = 50 µAV-2, (W / L) = 20, VTn = 1 V, then VOUT = 1.45 V for IOUT = 0 A. * Stack up two diode-connected MOSFETs EE 105 Spring 2000 Page 2 Week 11, Lecture 26 Totem Pole Voltage Sources * Define a series of bias voltages between the positive and the negative supply voltages. * In practice, output currents are small (or zero), so that the DC bias voltages are set by IREF EE 105 Spring 2000 Page 3 Week 11, Lecture 26 MOSFET Current Sources * Bias the n-channel MOSFET with a MOSFET DC voltage source! * Intuitively, VREF is set by IREF and determines the output current of M2 I REF V REF = V Tn + ------------------------------ = V GS1 = V GS2 W ------ µ C 2L 1 n ox Substituting into the drain current of M2 (and neglecting (1 + λnVDS2) term) 2 W i OUT = i D2 = ------ µ n C ox ( V GS2 – V Tn ) 2L 2 EE 105 Spring 2000 Page 4 Week 11, Lecture 26 MOSFET Current Sources (cont.) * Output current is scaled from IREF by a geometrical ratio: 2 I REF W i OUT = i D2 = ------ µ n C ox V Tn + -----------------------------V Tn – 2L 2 W ----- µ n C ox 2L 1 ( W ⁄ L ) 2 I OUT = -------------------- I REF ( W ⁄ L ) 1 EE 105 Spring 2000 Page 5 Week 11, Lecture 26 MOSFET Current Source Equivalent Circuit * Small-signal model: source resistance is ro2 by inspection * Combine output resistance with DC output current for approximate equivalent circuit ... actual iOUT vs. vOUT characteristics are those of M2 with VGS2 = VREF The model is only valid for vDS = vOUT > vDS(SAT) = VGS - VTn EE 105 Spring 2000 Page 6 Week 11, Lecture 26 The Cascode Current Source * In order to boost the source resistance, we can study our single-stage building blocks and recognize that a common-gate is attractive, due to its high output resistance * Adapting the output resistance for a common gate amplifier, the cascode current source has a source resistance of r oc = ( 1 + g m4 r o2 )r o4 ≈ g m4 r o4 r o2 * Penalty for cascode: needs larger VOUT to function EE 105 Spring 2000 Page 7 Week 11, Lecture 26 MOSFET Current “Mirrors” * n-channel current source sinks current to ground ... how do we source current from the positive supply? Answer: p-channel current sources...? * By mixing n-channel and p-channel diode-connected devices, we can produce current sinks and sources from a reference current connected to VDD or ground. EE 105 Spring 2000 Page 8 Week 11, Lecture 26 EE 105 Spring 2000 Page 9 Week 11, Lecture 26