* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbohydrates and Lipids
Survey
Document related concepts
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
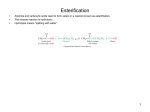
Macromolecules What is the relationship between atoms, bonding and macromolecules? Atoms join together Bonds that form Molecules that form large structures called Macromolecules Macromolecules and their subunits Monomer + Monomer + Monomer smaller subunits = Polymer = Macromolecule long chain of monomers glycogen glucose Macromolecules and their subunits Carbon Compounds 1 2 Carbohydrates Lipids Which are made of Which are made of Simple sugars (e.g., glucose) include Glycerol & 3 Fatty Acids 3 Nucleic acids (i.e. DNA/RNA) Which are made of Nucleotides which contain which contain which contain Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen Carbon, hydrogen oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus main function main function ENERGY STORAGE ENERGY STORAGE short-term long-term main function ENCODING HEREDITARY INFORMATION 4 Proteins Which are made of Amino Acids which contain Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, main function CATALYSIS & STRUCTURE /SUPPORT Carbohydrates Main Function: quick and short-term energy storage; also Carbon involved with structural support and cell-cell Compounds commonuication 1 3 4 Nucleic acids Proteins include 2 Groupings: C, H, and O atoms Carbohydrates Which are made of Lipid Two types:s 1. Simple Simple sugars (e.g., glucose) (1 : 2 : 1 ratio) Carbohydrates Which are made 2.ofComplex Carbohydrates Which are made of Glycerol & 3 Fatty Acids Nucleotides Which are made of (4 Acids cal/g) Amino which contain which contain which contain which contain Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen Carbon, hydrogen oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, main function ENERGY STORAGE short-term Carbohydrates – Simple (glucose) Carbohydrate molecule with 3-7 carbon atoms is called monosaccharide. (mono = one, saccharide = sugar); contains a single sugar Broken down quickly in the body to release energy. e.g., GLUCOSE – hexose (six-carbon) sugar with 7 energy-storing C-H bonds 6 5 4 1 3 Primary source of energy used by all cells 2 C6H12O6 (ring structure – when dissolved in water) Carbohydrates – Simple (glucose) Monosaccharides that contain 3C, 5C, & 6C are the most common All monosaccharides exist in linear form, when in water, monosaccharides with 5 or more carbons can fold to form a ring structure EX. Glucose: carbonyl group interacts with a hydroxyl group Carbohydrates – Simple (glucose) When glucose forms a ring, there are two possible arrangements Humans can digest (starches) Humans cannot digest (cellulose) These are isomers (a molecule that has the same composition but a different arrangement) with different properties Making & Breaking Carbohydrates monosaccharide + monosaccharide disaccharide (di = two) Condensation (dehydration) synthesis Hydrolysis Making & Breaking Carbohydrates 1-4 -linkage Glycosidic bond – a bond between monosaccharides 1-5 -linkage 1-4 -linkage Carbohydrates – Complex (Polysaccharides) Main Function: quick and short-term energy storage (starch/glycogen); structural support (cellulose/chitin) Contain many units of monosaccharides in long chains Polymerization is the process in which smaller molecules (monomers) link together to form a larger molecule (polymer) Carbohydrates – Complex (Polysaccharides) Starch, Starch = energy storage in plants Starch Granules (purple) in Potato Cells Carbohydrates – Complex (Polysaccharides) Glycogen (polymer) Glycogen = energy storage in animals muscle liver Glycogen (red) in Hepatocytes (liver cells) Carbohydrates – Complex (Polysaccharides) Cellulose fibers Cellulose = polysaccharide found in plant cell walls = contain numerous polar OH- groups that allow them to assemble side by side to enable strength =hydrophilic but do not dissolve Carbohydrates – Complex (Polysaccharides) Chitin Chitin = used to produce hard exoskeletons in insects and crustaceans Carbohydrates – Complex (Polysaccharides) What is the difference between starch and cellulose? Starch Cellulose Starch Glucose repeat units are facing the same direction Enzymes to digest Soluble Weaker Cellulose Both polymers Same monomer (glucose) Same repeat base Each successive glucose unit is upside-down in relation to each of the glucose molecules that it is connected to Cannot digest (no enzymes) Insoluble (fiber / roughage) Stronger (good for building) Carbohydrates and Lipids Section 1.4 Match the correct carbohydrate type to its structure. monosaccharide very long chain or branching chain with α or β linkage disaccharide two monomer subunits, with α or β linkage chain, α-ring, or β-ring polysaccharide Give two examples for each of three carbohydrate types above. Carbohydrates Section 1.4 Match the correct carbohydrate type to its structure. monosaccharide very long chain or branching chain with α or β linkage disaccharide two monomer subunits, with α or β linkage chain, α-ring, or β-ring polysaccharide Give two examples for each of three carbohydrate types above. monosaccharide: glucose and fructose disaccharide: lactose and sucrose polysaccharide: cellulose and starch Discussion: Carbohydrates and Lipids What are the functions of each carbohydrate type? Section 1.4 Discussion: Carbohydrates Section 1.4 What are the functions of each carbohydrate type? Monosaccharides and disaccharides are both primarily used as energy supplies. Polysaccharides are primarily used for energy storage, structural support, and cell-to-cell communication. Lipids (fats) Main Function: long-term energy storage; also use to 2 Lipids Which are made of regulate cellular activities. Special Feature: contain more energy per gram than any 3 other biological molecule (9 4 cal/g) Groupings: Mostly C and H atoms (hydrocarbons), smaller Nucleic amounts ofacids O Proteins Glycerol & 3 Fatty Acids which contain Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen main function ENERGY STORAGE long-term (e.g., Types: DNA/RNA) Which made ofAcids. 1.are Fatty Which are made of 2. Fats and oils Nucleotides 3. PhospholipidsAmino Acids 4. Steroids which contain which contain 5. Waxes Carbon, hydrogen oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus main function Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, main function CATALYSIS ENCODING & HEREDITARY STRUCTURE INFORMATION Plant oils (liquid @ room temp) /SUPPORT Animal fat (solid @ room temp) Lipids (fats) •Lipids are non-polar molecules and generally don’t dissolve in water Fatty Acids • The structural backbone of most lipids are fatty acids. • A fatty acid consists of a single hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl functional group (-COOH) at one end, giving the fatty acid acidic properties. • In living acids they contain 4 or more carbons in the hydrocarbon chain. • Commonly 14-22 carbons (in even-numbers) • The longer the chain, the less water soluble it is. # of double bonds between carbons Orientation State at Room Temp. Origin Which are better for you? Example Types of Fatty Acids Types of Fatty Acids # of Double Bonds between Carbons Saturated Unsaturated None (contains maximum # of H atoms) At least one double bond between carbon atoms Poly unsaturated Several double bonds Types of Fatty Acids Types of Fatty Acids Orientation of Fatty Acids Saturated Unsaturated Straight chains Kinks / bends at the double bonds Poly unsaturated Kinks / bends at the double bonds Types of Fatty Acids CH2-CH BEND DUE TO DOUBLE BOND Saturated vs. Unsaturated? Types of Fatty Acids Poly Saturated Unsaturated unsaturated Examples butter, lard olive oil, vegetable oil, peanut oil, canola oil # of double bonds between carbons Orientation State at Room Temp. Origin Which are better for you? Example Types of Fatty Acids Fats A fat is a lipid made from two types of molecules, a glycerol and a fatty acid 1 2 3 Glycerol Fatty acids Making and Breaking Lipids (fats) Making and Breaking Lipids (fats) Fats and oils are called triglycerides because of their structure What functional groups are present on the glycerol and fatty acid molecules? Hydrolysis Dehydration Synthesis + 3 H2O Saturated & Unsaturated Fats • Saturated Fat: a lipid that is composed of saturated fatty acids with a single bonds in their hydrocarbon chain • Unsaturated Fat: a lipid that is composed of unsaturated fatty acids with double bounds in their hydrocarbon chain Saturated & Unsaturated Fats Saturated Fats Unsaturated Fats • Obtained from animals • Solid at room temp. • Longer and straighter hydrocarbon chains; can be packed closer together • Store more energy • Obtained from plants • Liquid at room temp. (oils) • Hydrocarbon chains have kinks or bends (at double bonds) • Considered healthier for human diet Saturated & Unsaturated Fats Animal Fats vs. Fish Oils Saturated fats, which are typically solid at room temperature; however, warm-blooded mammals have liquid fat to enable movement Unsaturated fats, which are typically liquid at room temperature, enable fish to remain flexible and enable movement in colder temperatures Types of Fatty Acids Trans Fat Addition of hydrogen atoms to the acid, causing double bonds to become single ones. (unsaturated becomes saturated) LDL HDL Phospholipids Fat derivatives in which one fatty acid has been replaced by a phosphate group and one of several nitrogen-containing molecules. An important part of the cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer) Phospholipids Nitrogen-containing group Phospholipids The phospholipid can also be represented as: Non-Polar Tails (fatty acids) – hydrophobic (water-hating) Amphipathic Molecule: contains both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions Phospholipid Bilyer Steroids Differences in side groups distinguish one steroid from another Steroids Sterols (most abundant) have a simple single polar hydroxl group at one end and a complex non-polar hydrocarbon at the other end Almost completely hydrophobic, -OH gives some hydrophilic properties Cholesterol • Component of animal cell membranes •Can convert into Vitamin D • Contributes to atherosclerosis Waxes Long fatty acid chains linked to alcohols or carbon rings Hydrophobic, non-polar, and soft solids Often used as flexible waterproof coatings (i.e.cutin) Work • p. 38 – #1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7