* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download conserved in strong interactions
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Higgs mechanism wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Technicolor (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
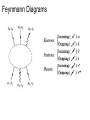
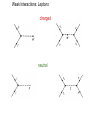
Quantum Electrodynamics Dirac Equation : spin 1/2 Feynmann Diagrams Moller Scattering Interaction is mediated by exchange of a photon Bhaba Scattering electron positron annhilation Symmetries, Groups and Conservation laws Closure: R1,R2 belong to G, R1.R2 also belongs to G Identity: There exists element I such that for all elements in G IRi=RiI=Ri Inverse: For every element there exists an inverse element such that RiRi-1=I Associativity: Symmetries and Conservation Laws Noether's theorem: Every continuous symmetry implies a corresponding conservation law and conversely, every conservation law reveals a symmetry in the system. Rotation ---- Angular momentum Time translation ----- Energy SU(2) Symmetry Group: Isospin • mass of proton ~ mass of neutron • treating proton as a different charge substrate of neutron: Isospin (I) I=1/2. (conserved in strong interactions) • I3 =+/- 1/2 -----> charge Q/e=1/2+ I3 • Analogous to a particle of ordinary spin 1/2 Generators of SU(2) are Pauli matrices: SU (3) symmetry: Flavour symmetry Generators of SU(3):Gell Mann Matrices Charge Conjugation: C Particle to antiparticle Parity Operation: P, reflects a system through the origin right handed system to left handed system axial system invariant under parity C and P are conserved in EM and Strong Interactions Time Reversal: T . Changes the direction of motion CPT invariance: All interactions are invariant under combined C,P,T Weak Interactions • • • • All quarks, leptons carry "weak charge" Short range interaction Interact via exchange of W+,W- and Z bosons (massive) two kinds of weak interactions: charged (W bosons) and neutral (Z boson) • Examples :decay processes Weak Interactions: Leptons charged neutral Conservation of electron, muon, tau numbers Conservation laws in WI • Conservation of charge • Conservation of Colour • Conservation of Baryon number • Electron, muon, tau number CP violation in Weak Interaction Weak Interactions are not always CP invariant. CP violation implies Time reversal must also be violated.