* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide For Unit 3 Test
Survey
Document related concepts
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Mechanics of planar particle motion wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
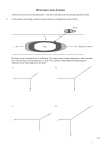
Honors Physics Study Guide for the Unit 3 Test Content overview Kinematics o 5 Problem solving steps o Graph models and math models o Zones Vectors/Scalars o 3 representations Draw to scale with reference axes Identify magnitude & direction Sum of perpendicular components o Tail-to-tip method of vector addition & subtraction o Resultant vectors AKA: Net vectors o Compass points and alternate types of axes Statics/Kinetics (Forces) o Names, types, & descriptions Weight (Fg) AKA: Gravitational force Fg = mg Long-range/non-contact due to the entire earth directed downward “m” refers to the mass of an object in kilograms “g” refers to the gravitational field strength in N/kg o At or near the earth’s surface, g = 9.8 N/kg Normal (FN) Contact force, exerted by a surface, directed perpendicular to the surface Magnetic (FM) Long-range/non-contact, due to the magnet Tension (FT) Contact force, exerted by a tether, directed along the tether Friction (FFR) Contact force, exerted by a surface, directed parallel to the surface to oppose motion o o o o o Agent/object notation Shorthand notation Subscripts ┴ or || Newton’s 1st law of motion ΣF = 0 ↔ ∆v = 0 If an object's velocity is not changing, the sum of the forces on the object is zero. If an object's velocity is changing, the sum of the forces on the object is not zero. This non-zero sum of forces is referred to as the “net force.” RECALL: Dry ice demo Newton’s 3rd law of motion Pairs of forces are exactly equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. RECALL: Stations lab Free-body diagrams Reduce object to a single point. Draw all force vectors acting on the object with the tails originating from the point. Honors Physics Study Guide for the Unit 3 Test 1. A paper airplane flies at 8 m/s 35o South of East. A) How fast did it fly in the south direction? B) How fast did it fly in the east direction? 2. A boat’s motor drives it due north 3 km, and a current pushes it west 1 km. A) What is the magnitude of the boat’s displacement? B) What is the specific direction of the boat’s displacement? 3. Draw a complete free body diagram using agent/object notation for a person leaning against a wall. 4. A standard gold bar has a mass of 12.4 kg. How much does it weigh? 5. A dragster accelerates from rest to 145 m/s in 4.5 seconds. Then, the dragster deploys a parachute slows it to a stop in 11 seconds. A) What is the acceleration during the first 4.5 seconds? B) What is the acceleration during the last 11 seconds? C) How far did the dragster travel total?