* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Learning Set 2 Vocabulary With Definitions (Study for test)
Survey
Document related concepts
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Work (thermodynamics) wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
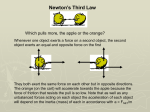
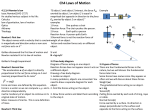
Name ________________________________________ Period _________ Date ____________ Vehicles in Motion Learning Set Two Vocabulary Propulsion System – A set of parts that produce a force to make an object move forward Work – when a force exerted on an object causes the object to move in the same direction as the force. Energy – the capacity to move something from an at rest position. Energy has many different forms. Kinetic Energy – The energy associated with an object in motion. Potential Energy – The energy that is stored in an object as a result of its position or condition Variable – A quantity whose value may change (vary) over the course of an experiment Independent Variable (Manipulated) – in an experiment, a variable whose value is manipulated, or changed, by the experimenter, to observe its effects on another variable Dependent Variable (Responding) – in an experiment, a variable whose value changes when the value of the independent variable is changed. Controlled Variables – In an experiment, the variables that are kept the same each time the procedure is performed. Hypothesis – a prediction of what will happen between an independent variable and a dependent variable. Trend – A general direction in which something tends to change; also, the way the dependent variable tends to change when the independent variable is changed Action Force – a force exerted by one object on a second object Reaction Force – the equal, but opposite, force exerted by the second object back on the first object in response to an action force Contact Force – A force that acts between two objects that are directly touching. The normal force is an example of a contact force. Non-Contact Force – A force that acts between objects that are not touching. Gravity is an example of a non-contact force. Spring Scale – a toll used by scientists to measure the size (magnitude) of a force by how much it stretches a spring Newton (N) – A unit of measurement for forces. Weightless – having little or no apparent gravitational pull Mass – the amount of matter in an object Weight – the force of an object due to gravity Attraction – the force that draws objects together Newton’s First Law of Motion – an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in at a constant speed in the same direction unless an unbalanced force acts on it. Newton’s Second Law of Motion – the acceleration of an object depends on the magnitude of the net force acting on it and the mass of the object. Newton’s Third Law of Motion – for every force exerted on an object a force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction is also exerted by the object