* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Crusades
Survey
Document related concepts
Church of the Holy Sepulchre wikipedia , lookup
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Rhineland massacres wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Nicopolis wikipedia , lookup
Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Arsuf wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Second Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1189–1191) wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
First Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
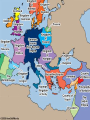
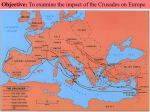
The Crusades An extended religious war fought between Christian and Muslim forces for possession of Jerusalem and the Holy Land 1095-1291 The rundown… • European Christians (England, France, Italy, Germany, & Turkey) • vs. Middle Eastern Muslims (Palestine, Syria, Egypt, & North Africa) • Fought mostly in Anatolia (Turkey), the Holy Land, & Egypt • Led to clash of Eastern vs. Western cultures and exchange of ideas, food, etc. Key Events • 634-44: Holy Land conquered by Muslims • 1095: Byzantine emperor asks Pope for help • 1096: First Crusade begins • 1099: Jerusalem captured by Christians • 1147: Second Crusade begins • 1187: Jerusalem captured by Muslims • 1189: Third Crusade begins • 1204: Crusaders sack Constantinople • 1291: Last crusader outpost in Holy Land, Acre, falls Strategy Crusaders • Recapture Holy Land in name of Christianity • Organized territory on feudal lines • Defend conquests in Holy Land with castle • Turn European aggression outward • Offer immediate forgiveness of sins to Crusaders Muslims • Repulse Christian attacks • Avoid civil wars between Muslim states Tactics Crusaders • Center of attack was charge of heavy cavalry (knights) • Shock of heavy cavalry charge was meant to shatter the enemy • Foot soldiers, archers used to support main attack Muslims • Widely used fast moving mounted archers • Main component of army was Mamluks (turkish military slaves) Technology Crusaders • Lances • Swords • Iron helmets and chain mail tunics • Kite-shaped shields • Footsoldiers armed with what they could afford • crossbows Muslims • Lightly armored, leather or horn tunics • Iron helmets • Heavy cavalry had chain mail • Composite bows Leadership Crusaders • GUY OF LUSIGNAN – King of Jerusalem 1185 – Attempted to relieve garrison at Tiberias – Marched army from sources of water – Crushed at Battle of Hattin by Saladin – Led to Muslim conquest of Jerusalem • RICHARD THE LIONHEART – King of England (spent only 6 months of his reign in England) – Led 3rd Crusade, forced to sue for peace with Saladin Muslims • SALADIN – Kurdish Muslim who unified Egypt & Syria after sezing power in 1174 – United Muslims against Crsuaders – Captured Jerusalem around 1187 – Employed scorched earth methods against Richard – His chivalrous actions led to his legend during the Crusades Logistics Crusaders • Establish bases in Holy Land • Depended on influx of European soldiers motivated by religion and/or greed • Distance from Europe made success difficult Muslims • Wear down Crusader armies • Depended on Mamluks and other soldiers from nearby Middle Eastern states • Benefitted from geographical location “home turf” Military Orders • Several religious military orders were formed in the Holy Land during the Crusades – Templars – Hospitallers – Teutonic Knights The Northern Crusade